Appearance
关于sass(scss)、less、postcss、stylus的简介和区别
为什么会出现css预处理器
比如一个项目的主题色在很多地方引用,后面需要修改,就得改很多个地方,难以维护。css预处理器就是解决类似问题的。
css预处理器的本质
它会通过编译器最终编译成浏览器可以识别的CSS文件。比较优秀的有:sass、less、stylus。
sass
sass是一种动态样式语言,由Ruby开发者设计和开发,比CSS多出好些功能,比如变量、嵌套、运算、混入、继承、指令、颜色处理、函数等。
sass与scss的关系
sass从第三代开始,放弃了缩进风格,并且完全向下兼容普通的css代码,这一代的sass也被称为scss。
sass/scss与less、stylus的区别
编译环境不一样
Sass需要Ruby环境
Less需要引入less.js
Stylus需要安装node
变量符不一样
Sass
$color:#eee;
Less
@color:#eee;
Stylus
mainColor:#eee;
输出风格
SASS的输出风格有四种:
nested,嵌套缩进的CSS代码,默认值
expanded,展开的多行CSS代码
compact,简洁格式的CSS代码
compressed,压缩后的CSS代码
总结
使用CSS预处理是为了让CSS代码更好维护,开发更加灵活、强大。
vscode集成sass
安装插件
安装Live Sass Compiler这个插件,进行一些配置,打开下面这个地址
https://github.com/ritwickdey/vscode-live-sass-compiler
找到Settings=>Settings Docs,点击打开,复制里面的配置
js
"liveSassCompile.settings.formats":[
{
/*
nested:嵌套格式
expanded:展开格式
compact:紧凑格式
compressed:压缩格式
*/
"format": "expanded", // 可定制的出口CSS样式(expanded,compact,compressed,nested)
"extensionName": ".css",
"savePath": "~/../css" // null表示当前目录
}
],
/*排除目录*/
"liveSassCompile.settings.excludeList":[
"**/node_modules/**",
".vscode/**"
],
/*是否生成对应的map*/
"liveSassCompile.settings.generateMap": true,
/*是否添加兼容前缀,例如:-webkit- -moz-等*/
"liveSassCompile.settings.autoprefix": [
"> 1%",
"last 2 versions"
]找到这个插件,点击拓展设置
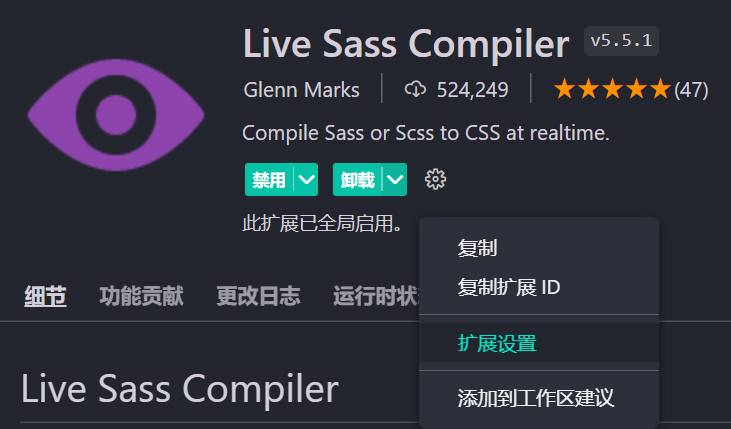
紧接着在settings.json中设置,将刚才的代码粘贴进去
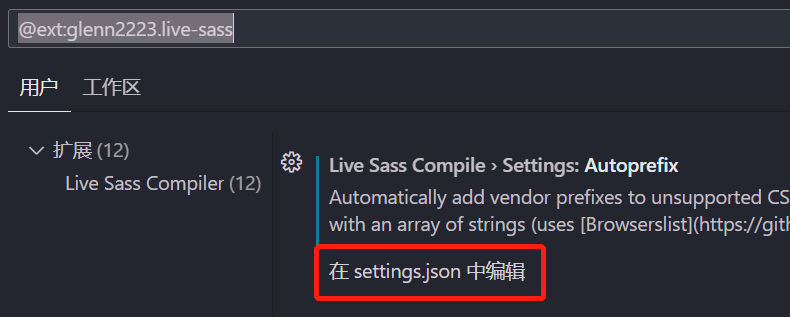
将scss编译成css
点击vscode下面的Watchs Sass,就会将scss转为css
sass的几种输出格式
这个就是改上面settings.json中的format的值,编译出来的CSS会展示不同的格式
对下面这段代码设置不同的format值,编译展示不同的CSS
css
html {
font-size: 12px;
color: #333;
.container {
font-size: 14px;
.header {
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
.left {
float: left;
}
}
.footer {
background-color: green;
}
&::after {
display: inline-block;
}
}
}比如将设置format为expanded:展开格式,那么将编译为
css
html {
font-size: 12px;
color: #333;
}
html .container {
font-size: 14px;
}
html .container .header {
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
}
html .container .header .left {
float: left;
}
html .container .footer {
background-color: green;
}
html .container::after {
display: inline-block;
}sass语法功能扩张
选择器嵌套
有下面这段css代码,如何改造成scss代码
css
.container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.container .header {
height: 90px;
line-height: 90px
}
.container .header .logo {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
.container .center {
height: 60px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.container .footer {
font-size: 16px;
text-align: center;
}用scss就可以这样写
css
.container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
.header {
height: 90px;
line-height: 90px;
.logo {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
}
.center {
height: 60px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.footer {
font-size: 16px;
text-align: center;
}
}编译出来的css代码和上面一样
父选择器&
再来看下面这段css代码,如何改造成scss
css
.container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.container a {
color: #333;
}
.container a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
color: #f00;
}
.container .top {
border: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
}
.container .top-left {
float: left;
width: 200px;
}可以这样写
css
.container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
a {
color: #333;
&:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
color: #f00;
}
}
.top {
border: 1px solid #f2f2f2;
&-left {
float: left;
width: 200px;
}
}
}属性嵌套
还有下面这段css代码,如何改写
css
.container a {
color: #333;
font-size: 14px;
font-family: serif;
font-weight: bold;
}可以这么写
css
.container {
a {
color: #333;
font: {
size: 14px;
family: serif;
weight: bold;
}
}
}占位符选择器%必须通过@extend
下面这段scss代码正常是不会编译
css
.button%base {
display: inline-block;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-weight: normal;
text-align: center;
white-space: nowrap;
vertical-align: middle;
-ms-touch-action: manipulation;
touch-action: manipulation;
cursor: pointer;
background-image: none;
border: 1px solid transparent;
padding: 6px 12px;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.42857143;
border-radius: 4px;
-webkit-user-select: none;
-moz-user-select: none;
-ms-user-select: none;
user-select: none;
}但是如果使用@extend就会被编译
css
.button%base {
display: inline-block;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-weight: normal;
text-align: center;
white-space: nowrap;
vertical-align: middle;
-ms-touch-action: manipulation;
touch-action: manipulation;
cursor: pointer;
background-image: none;
border: 1px solid transparent;
padding: 6px 12px;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.42857143;
border-radius: 4px;
-webkit-user-select: none;
-moz-user-select: none;
-ms-user-select: none;
user-select: none;
}
.btn-default {
@extend %base;
color: #333;
background-color: #fff;
border-color: #ccc;
}
.btn-success {
@extend %base;
color: #fff;
background-color: #5cb85c;
border-color: #4cae4c;
}
.btn-danger {
@extend %base;
color: #fff;
background-color: #d9534f;
border-color: #d43f3a;
}经过编译就会变成下面这样
css
.button.btn-danger, .button.btn-success, .button.btn-default {
display: inline-block;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-weight: normal;
text-align: center;
white-space: nowrap;
vertical-align: middle;
-ms-touch-action: manipulation;
touch-action: manipulation;
cursor: pointer;
background-image: none;
border: 1px solid transparent;
padding: 6px 12px;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.42857143;
border-radius: 4px;
-webkit-user-select: none;
-moz-user-select: none;
-ms-user-select: none;
user-select: none;
}
.btn-default {
color: #333;
background-color: #fff;
border-color: #ccc;
}
.btn-success {
color: #fff;
background-color: #5cb85c;
border-color: #4cae4c;
}
.btn-danger {
color: #fff;
background-color: #d9534f;
border-color: #d43f3a;
}sass的两种注释
单行注释
// 不会编译到css中
多行注释
/**/ 会被编译到css中
sass变量详解
css变量的定义与书写
css
:root {
--color: #F00;
}
body {
--border-color: #f2f2f2;
}
.header {
--background-color: #f8f8f8;
}
p {
color: var(--color);
border-color: var(--border-color);
}
.header {
background-color: var(--background-color);
}SASS的写法
css
$font-size:14px;
.container {
font-size: $font-size;
}sass变量的定义
定义规则
- 变量以美元符号($)开头,后面跟变量名;
- 变量名是不以数字开头的可包含字母、数字、下划线、横线(连接符);
- 写法同css,即变量名和值之间用冒号(:)分隔;
- 变量一定要先定义,后使用;
连接符与下划线
通过连接符与下划线 定义的同名变量为同一变量,建议使用连接符
css
$font-size:14px;
$font_size:16px;
.container{font-size: $font-size;}上面这段scss代码会被编译成
css
.container {
font-size: 16px;
}变量的作用域
局部变量
定义:在选择器内容定义的变量,只能在选择器范围内使用
css
.container {
$font-size: 14px;
font-size: $font-size;
}会编译成
css
.container {
font-size: 14px;
}全局变量
定义后能全局使用的变量
第一种:在选择器外面的最前面定义的变量
css
$font-size:16px;
.container {
font-size: $font-size;
}
.footer {
font-size: $font-size;
}会编译成
css
.container {
font-size: 16px;
}
.footer {
font-size: 16px;
}第二种:使用 !global 标志定义全局变量
css
.container {
$font-size: 16px !global;
font-size: $font-size;
}
.footer {
font-size: $font-size;
}会编译成
css
.container {
font-size: 16px;
}
.footer {
font-size: 16px;
}变量值类型
变量值的类型可以有很多种
SASS支持 7 种主要的数据类型
- 数字,1, 2, 13, 10px,30%
- 字符串,有引号字符串与无引号字符串,"foo", 'bar', baz
- 颜色,blue, #04a3f9, rgba(255,0,0,0.5)
- 布尔型,true, false
- 空值,null
- 数组 (list),用空格或逗号作分隔符,1.5em 1em 0 2em, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif
- maps, 相当于 JavaScript 的 object,(key1: value1, key2: value2)
例如
css
$layer-index:10;
$border-width:3px;
$font-base-family:'Open Sans', Helvetica, Sans-Serif;
$top-bg-color:rgba(255,147,29,0.6);
$block-base-padding:6px 10px 6px 10px;
$blank-mode:true;
$var:null; // 值null是其类型的唯一值。它表示缺少值,通常由函数返回以指示缺少结果。
$color-map: (color1: #fa0000, color2: #fbe200, color3: #95d7eb);
$fonts: (serif: "Helvetica Neue",monospace: "Consolas");使用
css
.container {
$font-size: 16px !global;
font-size: $font-size;
@if $blank-mode {
background-color: #000;
}
@else {
background-color: #fff;
}
content: type-of($var);
content:length($var);
color: map-get($color-map, color2);
}
.footer {
font-size: $font-size;
}
// 如果列表中包含空值,则生成的CSS中将忽略该空值。
.wrap {
font: 18px bold map-get($fonts, "sans");
}会编译成
css
.container {
font-size: 16px;
background-color: #000;
content: null;
content: 1;
color: #fbe200;
}
.footer {
font-size: 16px;
}
.wrap {
font: 18px bold;
}默认值
$color:#333;
// 如果$color之前没定义就使用如下的默认值
$color:#666 !default;
.container {
border-color: $color;
}sass导入@import详解
@import
Sass 拓展了 @import 的功能,允许其导入 SCSS 或 Sass 文件。被导入的文件将合并编译到同一个 CSS 文件中,另外,被导入的文件中所包含的变量或者混合指令 (mixin) 都可以在导入的文件中使用。
例如
public.scss
css
$font-base-color:#333;在index.scss里面使用
css
@import "public";
$color:#666;
.container {
border-color: $color;
color: $font-base-color;
}**注意:**跟我们普通css里面@import的区别
如下几种方式,都将作为普通的css语句,不会导入任何 sass 文件
- 文件拓展名是 .css;
- 文件名以 http:// 开头;
- 文件名是 url();
- @import 包含 media queries。
css
@import "public.css";
@import url(public);
@import "http://xxx.com/xxx";
@import 'landscape' screen and (orientation:landscape);局部文件(partials)
Sass源文件中可以通过@import指令导入其他Sass源文件,被导入的文件就是局部文件,局部文件让Sass模块化编写更加容易。
如果一个目录正在被Sass程序监测,目录下的所有scss/sass源文件都会被编译,但通常不希望局部文件被编译,因为局部文件是用来被导入到其他文件的。如果不想局部文件被编译,文件名可以以下划线 (_)开头
例如:
_theme.scss
css
$border-color:#999;
$background-color:#f2f2f2;使用
css
@import "theme";
.container {
border-color: $border-color;
background-color: $background-color;
}可以看到,@import 引入的theme.scss,可以没有下划线,这是允许的,这也就意味着,同一个目录下不能同时出现两个相关名的sass文件(一个不带下划线,一个带下划线),添加下划线的文件将会被忽略。
嵌套 @import
大多数情况下,一般在文件的最外层(不在嵌套规则内)使用 @import,其实,也可以将 @import 嵌套进 CSS 样式或者 @media 中,与平时的用法效果相同,只是这样导入的样式只能出现在嵌套的层中。
例如
_base.scss
css
.main-color {
color: #F00;
}使用
css
.container {
@import "base";
}注意:@import不能嵌套使用在控制指令或混入中
sass混合指令 (mixin directives)
混合指令(Mixin)用于定义可重复使用的样式。混合指令可以包含所有的 CSS 规则,绝大部分 Sass 规则,甚至通过参数功能引入变量,输出多样化的样式。
定义与使用混合指令 @mixin
css
@mixin mixin-name() {
/* css 声明 */
}例1:标准形式
定义
css
// 定义页面一个区块基本的样式
@mixin block {
width: 96%;
margin-left: 2%;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 1px #f6f6f6 solid;
}使用
css
.container {
@include block;
}会被编译成
css
.container {
width: 96%;
margin-left: 2%;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 1px #f6f6f6 solid;
}例2:嵌入选择器
例如
css
// 定义警告字体样式,下划线(_)与横线(-)是一样的
@mixin warning-text {
.warn-text {
font-size: 12px;
color: rgb(255, 253, 123);
line-height: 180%;
}
}使用
css
// 使用混入
.container {
@include warning-text();
}会被编译成
css
.container .warn-text {
font-size: 12px;
color: rgb(255, 253, 123);
line-height: 180%;
}例3:使用变量
定义
css
// 定义flex布局元素纵轴的排列方式
@mixin flex-align($aitem) {
-webkit-box-align: $aitem;
-webkit-align-items: $aitem;
-ms-flex-align: $aitem;
align-items: $aitem;
}使用
css
// 只有一个参数,直接传递参数
.container {
@include flex-align(center);
}
// 给指定参数指定值
.footer {
@include flex-align($aitem: center);
}例4:使用变量(多参数)
例如
css
// 定义块元素内边距
@mixin block-padding($top, $right, $bottom, $left) {
padding-top: $top;
padding-right: $right;
padding-bottom: $bottom;
padding-left: $left;
}使用一
css
// 按照参数顺序赋值
.container {
@include block-padding(10px, 20px, 30px, 40px);
}使用二
css
// 可指定参数赋值
.container {
@include block-padding($left: 20px, $top: 10px, $bottom: 10px, $right: 30px);
}使用三:只设置两边
css
// 可指定参数赋值
.container {
@include block-padding($left: 10px, $top: 10px, $bottom: 0, $right: 0);
}**问题:**必须指定4个值
例5:指定默认值
定义
css
// 定义块元素内边距,参数指定默认值
@mixin block-padding($top:0, $right:0, $bottom:0, $left:0) {
padding-top: $top;
padding-right: $right;
padding-bottom: $bottom;
padding-left: $left;
}使用
css
// 可指定参数赋值
.container {
// 不带参数
//@include block-padding;
//按顺序指定参数值
//@include block-padding(10px,20px);
//给指定参数指定值
@include block-padding($left: 10px, $top: 20px)
}例6:可变参数
参数不固定的情况
css
/**
*定义线性渐变
*@param $direction 方向
*@param $gradients 颜色过度的值列表
*/
@mixin linear-gradient($direction, $gradients...) {
background-color: nth($gradients, 1);
background-image: linear-gradient($direction, $gradients);
}使用
css
.table-data {
@include linear-gradient(to right, #F00, orange, yellow);
}会编译成
css
.table-data {
background-color: #F00;
background-image: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, right top, from(#F00), color-stop(orange), to(yellow));
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #F00, orange, yellow);
}@mixin混入总结
- mixin是可以重复使用的一组CSS声明
- mixin有助于减少重复代码,只需声明一次,就可在文件中引用
- 混合指令可以包含所有的 CSS 规则,绝大部分 Sass 规则,甚至通过参数功能引入变量,输出多样化的样式。
- 使用参数时建议加上默认值
什么时候用???? 很多地方都会用到却能根据不同场景灵活使用的样式
sass @extend(继承)指令
在设计网页的时候通常遇到这样的情况:一个元素使用的样式与另一个元素完全相同,但又添加了额外的样式。通常会在 HTML 中给元素定义两个 class,一个通用样式,一个特殊样式。
css案例
接下来以警告框为例进行讲解4种类型
| 标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| info | 信息!请注意这个信息。 |
| success | 成功!很好地完成了提交。 |
| warning | 警告!请不要提交。 |
| danger | 错误!请进行一些更改。 |
所有警告框的基本样式(风格、字体大小、内边距、边框等...) ,因为我们通常会定义一个通用alert样式
css
.alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}不同警告框单独风格
css
.alert-info {
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}使用
css
<div class="alert alert-info">
信息!请注意这个信息。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-success">
成功!很好地完成了提交。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-warning">
警告!请不要提交。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-danger">
错误!请进行一些更改。
</div>使用继承@extend改进
基本样式我们没有变,主要是各个警告框单独的样式
css
.alert-info {
@extend .alert;
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
@extend .alert;
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
@extend .alert;
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
@extend .alert;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}会被编译成
css
// 继承.alert的样式
.alert, .alert-danger, .alert-warning, .alert-success, .alert-info {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.alert-info {
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}使用时就不须要再写基本类了
css
<div class="alert-info">
信息!请注意这个信息。
</div>
<div class="alert-success">
成功!很好地完成了提交。
</div>
<div class="alert-warning">
警告!请不要提交。
</div>
<div class="alert-danger">
错误!请进行一些更改。
</div>使用多个@extend
定义两个类
css
.alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.important {
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 14px;
}使用
css
.alert-danger {
@extend .alert;
@extend .important;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}@extend多层继承
第一层继承
css
.alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.important {
@extend .alert;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 14px;
}再继承
css
.alert-danger {
@extend .important;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}占位符%
你可能发现被继承的css父类并没有被实际应用,也就是说html代码中没有使用该类,它的唯一目的就是扩展其他选择器。
对于该类,可能不希望被编译输出到最终的css文件中,它只会增加CSS文件的大小,永远不会被使用。
这就是占位符选择器的作用。
占位符选择器类似于类选择器,但是,它们不是以句点(.)开头,而是以百分号(%)开头。
当在Sass文件中使用占位符选择器时,它可以用于扩展其他选择器,但不会被编译成最终的CSS。
改写
css
%alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.alert-info {
@extend %alert;
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
@extend %alert;
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
@extend %alert;
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
@extend %alert;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}编译结果为
css
// 可以看到这里没有编译.alert
.alert-danger, .alert-warning, .alert-success, .alert-info {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.alert-info {
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}还可以使用@minix进行改进
css
@mixin alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.alert-info {
@include alert;
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
@include alert;
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
@include alert;
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
@include alert;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}最终编译成
css
.alert-info {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}可以看到相当于把.alert样式都混入到各自的样式中,相较于继承来说,并不是那么友好。
sass 运算 (operations)符的基本使用
等号操作符
所有数据类型都支持等号运算符:
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| == | 等于 |
| != | 不等于 |
例1数字比较:
css
$theme:1;
.container {
@if $theme==1 {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}例2字符串比较:
css
$theme:"blue";
.container {
@if $theme !="blue" {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}所有数据类型均支持相等运算 == 或 !=,此外,每种数据类型也有其各自支持的运算方式。
关系(比较)运行符
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| < (lt) | 小于 |
| > (gt) | 大于 |
| <= (lte) | 小于等于 |
| >= (gte) | 大于等于 |
例
css
$theme:3;
.container {
@if $theme >= 5 {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}逻辑运行符
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| and | 逻辑与 |
| or | 逻辑或 |
| not | 逻辑非 |
例
css
$width:100;
$height:200;
$last:false;
div {
@if $width>50 and $height<300 {
font-size: 16px;
}
@else {
font-size: 14px;
}
@if not $last {
border-color: red;
}
@else {
border-color: blue;
}
}数字操作符
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| + | 加 |
| - | 减 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
| % | 取模 |
例
css
/*
+、-、*、/、%
线数字、百分号、css部分单位(px、pt、in...)
+
线数字与百分号或单位运算时会自动转化成相应的百分比与单位值
*/
.container {
/* ==================+ 运算===================== */
width: 50 + 20; // 70
width: 50 + 20%; // 70%
width: 50% + 20%; // 70%
width: 10px + 20px; // 30px
width: 10pt + 20px; // 25pt (1px=3/4pt)
width: 10pt + 20; // 30pt
width: 10px + 10; // 20px
/* ==================- 运算===================== */
height: 50 - 30; // 20
height: 10 - 30%; // -20%
height: 60% - 30%; // 30%
height: 50px - 20px; // 30px
height: 50pt - 20px; // 35pt
height: 50pt - 40; // 10pt
/* ==================* 运算===================== */
height: 50 * 30; // 1500
height: 10 * 30%; // 300%
/* height: 60% * 30%; 出现了两个百分号*/
/* height: 50px * 20px; 出现了两个单位*/
height: 50 * 2px; // 100px
height: 50pt * 4; // 200pt
/* ==================/运算 (除完后最多只能保留一种单位)===================== */
$width: 100px;
width: 10 / 5; // 10/5
width: 10px / 5px; // 10px/5px
width: 10px / 10 * 2; // 2px
width: 20px / 2px * 5%; // 50%
width: ($width/2); // 使用变量与括号 50px
z-index: round(10)/2; // 使用了函数 // 5
height: (500px/2); // 使用了括号 // 250px
/* ==================% 运算===================== */
width: 10 % 3; // 1
width: 50 % 3px; // 2px
width: 50px % 4px; // 2px
width: 50px % 7; // 1px
width: 50% % 7; // 1%
width: 50% % 9%;// 5%
width: 50px % 10pt; // 50px % 13.33333px = 10px
width: 50px % 13.33333px; // 10.00001px
width: 50px + 10pt; // 63.3333333333px
/* width: 50px % 5%; 单位不统一*/
}/ 在 CSS 中通常起到分隔数字的用途,SassScript 作为 CSS 语言的拓展当然也支持这个功能,同时也赋予了 / 除法运算的功能。也就是说,如果 / 在 SassScript 中把两个数字分隔,编译后的 CSS 文件中也是同样的作用。
以下三种情况 / 将被视为除法运算符号:
- 如果值或值的一部分,是变量或者函数的返回值
- 如果值被圆括号包裹
- 如果值是算数表达式的一部分
例
css
$width: 1000px;
div {
font: 16px/30px Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; // 不运算
width: ($width/2); // 使用变量与括号
z-index: round(10)/2; // 使用了函数
height: (500px/2); // 使用了括号
margin-left: 5px + 8px/2px; // 使用了+表达式
}如果需要使用变量,同时又要确保 / 不做除法运算而是完整地编译到 CSS 文件中,只需要用 #{} 插值语句将变量包裹。
字符串运算
+ 可用于连接字符串
注意:如果有引号字符串(位于 + 左侧)连接无引号字符串,运算结果是有引号的,相反,无引号字符串(位于 + 左侧)连接有引号字符串,运算结果则没有引号。
css
.container {
content: "foo" + bar;
content: foo + "bar";
content: foo + bar;
content: "foo"+"bar";
}会编译成
css
.container {
content: "foobar";
content: foobar;
content: foobar;
content: "foobar";
}sass 插值语句 #{ }
引入之前的案例发出一个问题
例如
p{
font: 16px/30px Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}如果需要使用变量,同时又要确保 / 不做除法运算而是完整地编译到 CSS 文件中,只需要用 #{} 插值语句将变量包裹。
使用插值语法:
p {
$font-size: 12px;
$line-height: 30px;
font: #{$font-size}/#{$line-height} Helvetica,
sans-serif;
}通过 #{} 插值语句可以在选择器、属性名、注释中使用变量:
css
$class-name: danger;
$attr: color;
$author:'老姚';
/*
* 这是文件的说明部分
@author: #{$author}
*/
a.#{$class-name} {
border-#{$attr}: #F00;
}会被编译成
css
@charset "UTF-8";
/*
* 这是文件的说明部分
@author: 老姚
*/
a.danger {
border-color: #F00;
}sass 常见函数的基本使用
常见函数简介,更多函数列表可看:https://sass-lang.com/documentation/modules
Color(颜色函数)
sass包含很多操作颜色的函数。例如:lighten() 与 darken()函数可用于调亮或调暗颜色,opacify()函数使颜色透明度减少,transparent()函数使颜色透明度增加,mix()函数可用来混合两种颜色。
css
p {
height: 30px;
}
.p0 {
background-color: #5c7a29;
}
.p1 {
/*
让颜色变亮
lighten($color, $amount)
$amount 的取值在0% - 100% 之间
*/
background-color: lighten(#5c7a29, 30%);
}
.p2 {
// 让颜色变暗 通常使用color.scale()代替该方案
background-color: darken(#5c7a29, 15%);
}
.p3 {
// 降低颜色透明度 通常使用color.scale()代替该方案
// background-color: opacify(#5c7a29,0.5);
// 0.1和0.5这两个值,加起来不能超过1
background-color: opacify(rgba(#5c7a29, 0.1), 0.5);
}使用
html
<p></p>
<p class="p0"></p>
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2"></p>
<p class="p3"></p>String(字符串函数)
Sass有许多处理字符串的函数,比如向字符串添加引号的quote()、获取字符串长度的string-length()和将内容插入字符串给定位置的string-insert()。
例
css
p {
&:after {
content: quote(这是里面的内容); // 加引号
}
background-color: unquote($string: "#F00"); // 去掉字符串
z-index:str-length("sass学习"); // 计算字符串长度
}最终编译成
css
p {
background-color: #F00;
z-index: 6;
}
p:after {
content: "这是里面的内容";
}Math(数值函数)
数值函数处理数值计算,例如:percentage()将无单元的数值转换为百分比,round()将数字四舍五入为最接近的整数,min()和max()获取几个数字中的最小值或最大值,random()返回一个随机数。
例如
css
p {
z-index: abs($number: -15); // 15 绝对值
z-index: ceil(5.8); //6 向上取整
z-index: max(5, 1, 6, 8, 3); //8 获取最大值
opacity: random(); // 随机 0-1
}List函数
List函数操作List,length()返回列表长度,nth()返回列表中的特定项,join()将两个列表连接在一起,append()在列表末尾添加一个值。
例如:
css
p {
z-index: length(12px); //1 只有一个元素
z-index: length(12px 5px 8px); //3 有3个元素
z-index: index(a b c d, c); //3 c所在的位置
padding: append(10px 20px, 30px); // 10px 20px 30px 将30px追加到列表末尾
color: nth($list: red blue green, $n: 2); // blue 第2个位置是blue
}Map函数
Map函数操作Map,map-get()根据键值获取map中的对应值,map-merge()来将两个map合并成一个新的map,map-values()映射中的所有值。
css
$font-sizes: ("small": 12px, "normal": 18px, "large": 24px);
$padding:(top:10px, right:20px, bottom:10px, left:30px);
p {
font-size: map-get($font-sizes, "normal"); //18px
@if map-has-key($padding, "right") { // 判断是否有right这个key
padding-right: map-get($padding, "right");
}
&:after {
content: map-keys($font-sizes) + " "+ map-values($padding) + "";
}
}最终编译成
css
p {
font-size: 18px;
padding-right: 20px;
}
p:after {
content: '"small", "normal", "large" 10px, 20px, 10px, 30px';
}selector选择器函数
选择符相关函数可对CSS选择进行一些相应的操作,例如:selector-append()可以把一个选择符附加到另一个选择符,selector-unify()将两组选择器合成一个复合选择器。
例如
css
.header {
background-color: #000;
// 引号在前和在后返回的结果一样,和前面的字符串运算不一样
content: selector-append(".a", ".b", ".c") + "";
content: "" + selector-append(".a", ".b", ".c");
content: selector-unify("a", ".disabled") + "";
}最终编译成
css
.header {
background-color: #000;
content: ".a.b.c";
content: ".a.b.c";
content: "a.disabled";
}自检函数
自检相关函数,例如:feature-exists()检查当前Sass版本是否存在某个特性,variable-exists()检查当前作用域中是否存在某个变量,mixin-exists()检查某个mixin是否存在。
例如:
css
$color:#F00;
@mixin padding($left:0, $top:0, $right:0, $bottom:0) {
padding: $top $right $bottom $left;
}
.container {
// 注意:这里是color,不是$color
@if variable-exists(color) {
color: $color;
}
@else {
content: "$color不存在";
}
@if mixin-exists(padding) {
@include padding($left: 10px, $right: 10px);
}
}自检函数通常用在代码的调试上
sass 流程控制指令@if、@for、@each、@while
@if控制指令
@if()函数允许您根据条件进行分支,并仅返回两种可能结果中的一种。
语法方式同js的if....else if ...else
代码形式:
css
.container{
// 第一种
@if(/* 条件 */){
// ...
}
// 第二种
@if(/* 条件 */){
// ...
}@else{
// ...
}
// 第三种
@if(/* 条件 */){
// ...
}@else if(){
// ...
}@else{
// ...
}
}例1
css
$theme:"green";
.container {
@if $theme=="red" {
color: red;
}
@else if $theme=="blue" {
color: blue;
}
@else if $theme=="green" {
color: green;
}
@else {
color: darkgray;
}
}例如,定义一个css的三角形@mixin声明
css
@mixin triangle($direction:top, $size:30px, $border-color:black) {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: $size;
border-#{$direction}-width: 0;
@if ($direction==top) {
border-color: transparent transparent $border-color transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
@else if($direction==right) {
border-color: transparent transparent transparent $border-color;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
@else if($direction==bottom) {
border-color: $border-color transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
@else if($direction==left) {
border-color: transparent $border-color transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}
}使用
css
.p0 {
@include triangle();
}
.p1 {
@include triangle(right, 50px, red);
}
.p2 {
@include triangle(bottom, 50px, blue);
}
.p3 {
@include triangle(left, 50px, green);
}html
html
<p class="p0"></p>
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2"></p>
<p class="p3"></p>@if指令中的代码改进优化
css
@mixin triangle($direction:top, $size:30px, $border-color:black) {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: $size;
border-#{$direction}-width: 0;
@if ($direction==top) {
border-color: transparent transparent $border-color transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
@else if($direction==right) {
border-color: transparent transparent transparent $border-color;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
@else if($direction==bottom) {
border-color: $border-color transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
@else if($direction==left) {
border-color: transparent $border-color transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}
}
.p0 {
@include triangle();
}
.p1 {
@include triangle(right, 50px, red);
}
.p2 {
@include triangle(bottom, 50px, blue);
}
.p3 {
@include triangle(left, 50px, green);
}上面的代码会编译成
css
.p0 {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: 30px;
border-top-width: 0;
border-color: transparent transparent black transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
.p1 {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: 50px;
border-right-width: 0;
border-color: transparent transparent transparent red;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
.p2 {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: 50px;
border-bottom-width: 0;
border-color: blue transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
.p3 {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: 50px;
border-left-width: 0;
border-color: transparent green transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}通过观察,我们发现
css
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;这段代码是重复的,那么就可以使用继承指令的占位符
css
%triangle {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
}
@mixin triangle($direction:top, $size:30px, $border-color:black) {
border-width: $size;
border-#{$direction}-width: 0;
@if ($direction==top) {
border-color: transparent transparent $border-color transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
@else if($direction==right) {
border-color: transparent transparent transparent $border-color;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
@else if($direction==bottom) {
border-color: $border-color transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
@else if($direction==left) {
border-color: transparent $border-color transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}
}
.p0 {
@extend %triangle;
@include triangle();
}
.p1 {
@extend %triangle;
@include triangle(right, 50px, red);
}
.p2 {
@extend %triangle;
@include triangle(bottom, 50px, blue);
}
.p3 {
@extend %triangle;
@include triangle(left, 50px, green);
}最终编译出来的css代码,代码量就少很多,使用继承就是把公共的部分提取出去
css
.p3, .p2, .p1, .p0 {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
}
.p0 {
border-width: 30px;
border-top-width: 0;
border-color: transparent transparent black transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
.p1 {
border-width: 50px;
border-right-width: 0;
border-color: transparent transparent transparent red;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
.p2 {
border-width: 50px;
border-bottom-width: 0;
border-color: blue transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
.p3 {
border-width: 50px;
border-left-width: 0;
border-color: transparent green transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}@for指令
@for 指令可以在限制的范围内重复输出格式,每次按要求(变量的值)对输出结果做出变动。这个指令包含两种格式:@for $var from through ,或者 @for $var from to
区别在于 through 与 to 的含义:
- 当使用
through时,条件范围包含与的值。 - 而使用
to时条件范围只包含的值不包含 的值。 - 另外,$var 可以是任何变量,比如 $i; 和 必须是整数值。
例1
css
@for $i from 1 to 4 {
.p#{$i} {
width: 10px * $i;
height: 30px;
background-color: red;
}
}
@for $i from 1 through 3 {
.p#{$i} {
width: 10px * $i;
height: 30px;
background-color: red;
}
}使用
css
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2"></p>
<p class="p3"></p>例2:加载动画
css
#loading {
position: fixed;
top: 200px;
left: 46%;
}
#loading span {
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
background: #3498db;
opacity: 0.5;
border-radius: 50%;
animation: loading 1s infinite ease-in-out;
}
#loading span:nth-child(1) {
left: 0;
animation-delay: 0s;
}
#loading span:nth-child(2) {
left: 20px;
animation-delay: 0.2s;
}
#loading span:nth-child(3) {
left: 40px;
animation-delay: 0.4s;
}
#loading span:nth-child(4) {
left: 60px;
animation-delay: 0.6s;
}
#loading span:nth-child(5) {
left: 80px;
animation-delay: .8s;
}
@keyframes loading {
0% {
opacity: 0.3;
transform: translateY(0px);
}
50% {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(-20px);
background: green;
}
100% {
opacity: 0.3;
transform: translateY(0px);
}
}html
css
<div id="loading">
<span></span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
</div>用@for改进动画部分
css
@for $i from 1 to 5 {
#loading span:nth-child(#{$i}) {
left: 20 * ($i - 1) + px;
/* animation-delay: 20 * ($i - 1) / 100 + s; */
animation-delay: unquote($string: "0.") + ($i - 1) * 2 + s; // 去掉字符串
}
}@each指令
@each 指令的格式是 $var in , $var 可以是任何变量名,比如 $length 或者 $name,而 是一连串的值,也就是值列表。
例如做如下效果
普通CSS的写法
css
p{
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
display: inline-block;
margin: 10px;
}
.p0{
background-color: red;
}
.p1{
background-color: green;
}
.p2{
background-color: blue;
}
.p3{
background-color:turquoise;
}
.p4{
background-color: darkmagenta;
}用@each改进
css
$color-list:red green blue turquoise darkmagenta;
@each $color in $color-list {
$index: index($color-list, $color);
.p#{$index - 1} {
background-color: $color;
}
}@while 指令
@while 指令重复输出格式直到表达式返回结果为 false。这样可以实现比 @for 更复杂的循环。
用sass实现bootstrap中css的这么一段代码
https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.4.1/css/bootstrap.css
css
.col-sm-12 {
width: 100%;
}
.col-sm-11 {
width: 91.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-10 {
width: 83.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-sm-8 {
width: 66.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-7 {
width: 58.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-sm-5 {
width: 41.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-4 {
width: 33.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-sm-2 {
width: 16.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-1 {
width: 8.33333333%;
}用@while实现
css
$column:12;
@while $column>0 {
.col-sm-#{$column} {
width: $column / 12 * 100%;
// width: $column / 12 * 100 + %; 会标红
width: $column / 12 * 100#{"%"};
width: unquote($string: $column / 12 * 100 + "%");
}
$column:$column - 1;
}sass @function的使用
函数作用
把一些比较复杂或经常用些的内容进行抽离(封装),以便重复使用
函数的定义与使用
函数的定义
css
@function function-name([$param1,$param2,...]){
...
@return $value;
}提示:函数名function-name 与function_name 是相同的
@return
它只允许在@函数体中使用,并且每个@function必须以@return结束。当遇到@return时,它会立即结束函数并返回其结果。
例如:
下面这段css代码,如何用函数进行改写
css
.row-cols-1 > * {
width: 100%;
}
.row-cols-2 > * {
width: 50%;
}
.row-cols-3 > * {
width: 33.3333333333%;
}
.row-cols-4 > * {
width: 25%;
}
.row-cols-5 > * {
width: 20%;
}
.row-cols-6 > * {
width: 16.6666666667%;
}可以这样
css
@function row-cols-width($column) {
@return percentage(1 / $column);
}
@for $i from 1 through 6 {
.row-cols-#{$i}>* {
width: row-cols-width($i);
}
}函数的参数与默认值
css
/**
*定义线性渐变
*@param $direction 方向
*@param $gradients 颜色过度的值列表
*/
@function background-linear-gradient($direction, $start-color, $end-color:blue) {
@return linear-gradient($direction, $start-color, $end-color);
}正常传参调用
css
.header {
background-image: background-linear-gradient(to right, red, green);
}省略默认值
css
.header {
background-image: background-linear-gradient(to right, red);
}按照参数名传参
css
.header {
background-image: background-linear-gradient($start-color: red, $direction: to bottom);
}注意:函数参数默认值可以是任意SassScript表达式,甚至可以引用前面的参数
任意参数
参数任意参数
css
/**
*定义线性渐变
*@param $direction 方向
*@param $gradients 颜色过度的值列表
*/
@function background-linear-gradient($direction, $gradients...) {
@return linear-gradient($direction, $gradients);
}
.header {
background-image: background-linear-gradient(to bottom, red, green, blue);
}调用任意参数
css
$widths: 50px,30px,100px;
.logo {
width: min($widths...);
}混入mixin和函数function的区别
- 混入mixin主要是通过传递参数的方式输出多样化的样式,为了可以现实代码复用。
- 函数的功能主要是通过传递参数后,经过函数内部的计算,最后@return输出一个值。
三元条件函数if的使用
如何使用
css
if($condition,$if-true,$if-false);判断$condition,如果条件成立,则返回$if-true的结果,如果条件不成立,则返回$if-false的结果。
案例:
if的写法(浅色与深色模式)
css
$theme:'light';
.container {
@if $theme=='light' {
color: #000;
}
@else {
color: #FFF;
}
}三元条件函数if改进
css
$theme:'light';
.container {
color: if($theme=='light', #000, #FFF);
}sass @use 的使用
作用
从其他Sass样式表加载mixin,function和变量,并将来自多个样式表的CSS组合在一起,@use加载的样式表被称为“模块”,多次引入只包含一次。
@use也可以看作是对@import的增强
语法
@use '<url>' [as alias|namespace]加载普通scss、css
use下面的_common.scss
css
$font-size:14px !default;
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: $font-size;
color: #333;
}
@function column-width($col, $total) {
@return percentage($col/$total);
}
@mixin bgColor($bg-color:#f2f2f2) {
background-color: $bg-color;
}use下面的about.css
css
h1 {
font-size: 24px;
}使用
css
@use 'use/common';
@use 'use/about';加载模块
新增_global.scss
css
$font-size:28px;
@mixin base($color:#F00) {
color: $color;
}
.gclass {
background-color: #F00;
}@import的方式
css
@import 'use/common';
@import 'use/global';
@import 'use/global';
body {
font-size: $font-size;
@include base('#FFF');
@include base('#000');
width: column-width(3, 12);
@include bgColor('#F00');
}@use的方式
css
@use 'use/common';
@use 'use/global' as g1;
@use 'use/global' as g2;
body {
font-size: common.$font-size;
@include g1.base('#FFF');
@include g2.base('#000');
width: common.column-width(3, 12);
@include common.bgColor('#F00');
}通过@use引入的样式默认把文件名作为模块名使用,你可以通过as的形式重新取一个别名
@use取消别名
可能@use "" as * 来取消命名空间,这种方式加载的模块被提升为全局模块
注意:这种方式慎用
css
@use 'use/common';
@use 'use/global' as *;
@use 'use/global' as g2;
body {
font-size: $font-size;
@include base('#FFF');
@include g2.base('#000');
width: common.column-width(3, 12);
@include common.bgColor('#F00');
}定义私有成员
如果加载的模块内部有变量只想在模块内使用,可使用-或_定义在变量头即可
例如:
css
$-font-size:14px;
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: $-font-size;
color: #333;
}
@use 'use/common';
@use 'use/global' as *;
@use 'use/global' as g2;
body {
font-size: common.$-font-size; // 报错 Error: Private members can't be accessed from outside their modules.
@include base('#FFF');
@include g2.base('#000');
}定义默认值
通过!default能变量定义默认值
css
$font-size:14px !default;
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: $font-size;
color: #333;
}@use引入时可通过with(...)修改默认值
css
@use 'use/common' with ( $font-size:16px, );
@use 'use/global' as *;
@use 'use/global' as g2;
common.$font-size:28px; // 也可能通过这种方式覆盖
body {
font-size: common.$font-size;
@include base('#FFF');
@include g2.base('#000');
}默认加载index.scss
创建_index.scss
css
@use 'common' with ( $font-size:16px, );
@use 'global' as *;
@use 'global' as g2;
common.$font-size:28px; // 也可能通过这种方式覆盖
body {
font-size: common.$font-size;
@include base('#FFF');
@include g2.base('#000');
}使用
css
@use 'use/index';@use使用总结
- @use引入同一个文件多次,不会重复引入,而@import会重复引入
- @use引入的文件都是一个模块,默认以文件名作为模块名,可通过as alias取别名
- @use引入多个文件时,每个文件都是单独的模块,相同变量名不会覆盖,通过模块名访问,而@import变量会被覆盖
- @use方式可通过 @use 'xxx' as *来取消命名空间,建议不要这么做
- @use模块内可通过$- 或$来定义私有成员,也就是说或者-开头的Variables mixins functions 不会被引入
- @use模块内变量可通过!default 定义默认值,引入时可通用with(...)的方式修改
- 可定义-index.scss或_index.scss来合并多个scss文件,它@use默认加载文件
sass @forward的使用
作用
通过 @forward加载一个模块的成员,并将这些成员当作自己的成员对外暴露出去,类似于类似于 es6 的 export ...,通常用于跨多个文件组织 Sass 库
转发、合并scss
转发
创建forward/_common.scss
css
$font-size:14px !default;
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: $font-size;
color: #333;
}
@function column-width($col, $total) {
@return percentage($col/$total);
}
@mixin bgColor($bg-color:#f2f2f2) {
background-color: $bg-color;
}创建启动合并bootstrap.scss
css
@forward 'uses/common';使用
css
@use 'bootstrap';
.body {
font-size: bootstrap.$font-size;
width: bootstrap.column-width(3, 12);
@include bootstrap.bgColor('#F00');
}合并
新增一个_global.scss
css
$font-size:28px;
@mixin base($color:#F00) {
color: $color;
}
.gclass {
background-color: #F00;
}统一转发
css
@forward 'uses/common';
@forward 'uses/global';使用
css
@use 'bootstrap';
.body {
font-size: bootstrap.$font-size;
width: bootstrap.column-width(3, 12);
@include bootstrap.bgColor('#F00');
@include bootstrap.base('#000');
}**问题:**当多个被转发的文件存在相同变量、函数、混入时会有问题
选择性转发
默认情况下,@forward 会将一个模块中所有成员都转发,如果只想转发某些成员,当你不想转发所有变量、函数、混入时,可使用
@forward "module" hide $var, mixinName, fnName禁止转发某些成员@forward "module" show $var, mixinName, fnName只转发某些成员
各个成员通过逗号 , 分隔开,如果成员是变量,不能省略 $ 符号。
@forward 'uses/common' as com-* hide com-bgColor,$com-font-size;
@forward 'uses/global' as glob-* show base;使用
css
@use 'bootstrap';
.body {
font-size: bootstrap.$com-font-size;
width: bootstrap.com-column-width(3, 12);
@include bootstrap.com-bgColor('#000');
@include bootstrap.glob-base('#000');
}转发时定义前缀
@forward "" as -*
bootstrap.scs
css
@forward 'uses/common' as com-*;
@forward 'uses/global' as glob-*;使用
css
@use 'bootstrap';
.body {
font-size: bootstrap.$com-font-size;
width: bootstrap.com-column-width(3, 12);
@include bootstrap.com-bgColor('#F00');
@include bootstrap.glob-base('#000');
}转发时配置模块的成员
bootstarp
css
@forward 'uses/common' as com-* with ( $font-size:30px !default);
@forward 'uses/global' as glob-* show glob-base;使用
css
@use 'bootstrap' with ($com-font-size:50px);
.body {
font-size: bootstrap.$com-font-size;
width: bootstrap.com-column-width(3, 12);
@include bootstrap.com-bgColor('#000');
@include bootstrap.glob-base('#000');
}@use与@forward一起使用的情况
当一个模块里面须要同时使用@use与@forward时,建议先使用@forwar后再使用@use
css
@use 'uses/code';
@forward 'uses/common' as com-*;
@forward 'uses/global' as glob-* show glob-base;
@use 'use/common' as c1;
.test {
font-size: c1.$font-size;
color: code.$color;
}sass中@at-root使用
作用
@at-root可以使被嵌套的选择器或属性跳出嵌套
语法
css
@at-root <selector>{
...
}普通嵌套
css
.parent {
font-size: 12px;
.child {
font-size: 14px;
.son {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
}作用某个选择器使其跳出嵌套
css
.parent {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root .child {
font-size: 14px;
@at-root .son {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
}作用某些选择器使其跳出嵌套
css
.parent {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root {
.child-1 {
font-size: 14px;
}
.child-2 {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
}@at-root与&的结合使用
&的使用
css
.foo {
& .bar {
color: gray;
}
}
.foo {
& {
color: gray;
}
}
.foo {
.bar & {
color: gray;
}
}这跟前面加@at-root效果是一样的
使用@at-root结合#{&}实现BEM效果
理解BEM:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/122214519
官网学习:https://en.bem.info/methodology/quick-start/
BEM完整命名规则:block-name__element-name--modifier-name (也可以换成驼峰式命名)
官方网站最新推出:block-name__element-name_modifier-name
比较BEM的一则样式
css
.block{width: 1000px;}
.block__element{font-size: 12px;}
.block--modifier{font-size: 14px;}
.block__element--modifier{font-size: 16px;}实现
css
.block {
width: 1000px;
@at-root #{&}__element {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root #{&}--modifier {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
@at-root #{&}--modifier {
font-size: 14px;
}
}
//或
.block {
width: 1000px;
@at-root {
#{&}__element {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root #{&}--modifier {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
#{&}--modifier {
font-size: 14px;
}
}
}
// 实现上也能直接用&实现
.block {
width: 1000px;
&__element {
font-size: 12px;
&--modifier {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
&--modifier {
font-size: 14px;
}
}@at-root (without: …)和@at-root (with: …)的使用
默认@at-root只会跳出选择器嵌套,而不能跳出@media或@support,如果要跳出这两种,则需使用@at-root (without: media),@at-root (without: support)。这个语法的关键词有四个:
1、all(表示所有) 2、rule(表示常规css) 3、media(表示media) 4、supports(表示supports)
演示
css
@media screen {
.parent {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root (without: media) {
.child {
font-size: 14px;
.son {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
}
}
}
@supports (display: flex) {
.parent {
font-size: 12px;
@at-root (with: supports) {
.child {
font-size: 14px;
.son {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
}
}
}案例简单演示@at-root的用法
html
css
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>演示@at-root的用法</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/test.css">
</head>
<body>
<!-- 头部 -->
<header class="header">
<div class="logo">logo</div>
<form class="search-form">
<div class="content">
<input class="input" placeholder="搜索内容">
<button class="button">搜索</button>
</div>
</form>
</header>
<!-- 中间 -->
<div class="center"></div>
<!-- 底部 -->
<footer class="footer"></footer>
</body>
</html>简单的test.scss
css
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 750px;
max-width: 750px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
}
.header {
background-color: aquamarine;
height: 100px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 30px;
@at-root .logo {
font-size: 36px;
margin-right: 30px;
}
.search-form {
.content {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
.input {
padding: 4px 10px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.button {
border: none;
background-color: cadetblue;
color: #FFF;
height: 28px;
width: 60px;
}
}
}
}
.center {
flex: 1;
background-color: black;
}
.footer {
height: 200px;
background-color: burlywood;
}参考链接
B站地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ci4y1d74K/?p=1
sass 官方中文文档:https://www.sass.hk/docs/