Appearance
元素的属性和特性
前面我们已经学习了如何获取节点,以及节点通常所包含的属性,接下来我们来仔细研究元素Element。
我们知道,一个元素除了有开始标签、结束标签、内容之外,还有很多的属性(attribute)

浏览器在解析HTML元素时,会将对应的attribute也创建出来放到对应的元素对象上。
- 比如id、class就是全局的attribute,会有对应的id、class属性;
- 比如href属性是针对a元素的,type、value属性是针对input元素的;
接下来我们学习一下如何获取和设置这些属性。
attribute的分类
属性attribute的分类:
- 标准的attribute:某些attribute属性是标准的,比如id、class、href、type、value等;
- 非标准的attribute:某些attribute属性是自定义的,比如abc、age、height等;
html
<!-- 属性: attribute(特性) -->
<!--
attribute的分类:
1.如果是HTML标准制定的attribute, 称之为标准Attribute
2.而自定义的Attribute, 称之为非标准Attribute
-->
<div id="abc" class="box" title="box"
age="18" height="1.88">
我是box
</div>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>attribute的操作
对于所有的attribute访问都支持如下的方法:
- elem.hasAttribute(name) — 检查特性是否存在。
- elem.getAttribute(name) — 获取这个特性值。
- elem.setAttribute(name, value) — 设置这个特性值。
- elem.removeAttribute(name) — 移除这个特性。
- attributes:attr对象的集合,具有name、value属性。
attribute具备以下特征:
- 它们的名字是大小写不敏感的(id 与 ID 相同)。
- 它们的值总是字符串类型的。
html
<div id="abc" class="box" title="box"
age="18" height="1.88">
我是box
</div>
<input type="checkbox" checked="checked">javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 1.所有的attribute都支持的操作
console.log(boxEl.hasAttribute("AGE"), boxEl.hasAttribute("abc"), boxEl.hasAttribute("id")) // true false true
console.log(boxEl.getAttribute("AGE"), boxEl.getAttribute("abc"), boxEl.getAttribute("id")) // 18 null abc
boxEl.setAttribute("id", "cba") // id变成cba
boxEl.removeAttribute("id") // id没了
var boxAttributes = boxEl.attributes
for (var attr of boxAttributes) {
console.log(attr.name, attr.value)
}
// 2.通过getAttribute()一定是字符串类型
var inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
console.log(inputEl.getAttribute("checked")) // checked元素的属性(property)
html
<!-- 元素中的属性称之为attribute -->
<!-- 标准的attribute在对应的对象模型中都有对应的property -->
<div id="abc" class="box" title="标题"
age="18" height="1.88">
我是box
</div>
<input type="checkbox" checked>
账号: <input class="account" type="text">
<button class="btn">设置input的值</button>对于标准的attribute,会在DOM对象上创建与其对应的property属性:
javascript
// 1.通过property获取attribute的值
// 获取box元素
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
console.log(boxEl.id, boxEl.title, boxEl.age, boxEl.height) // abc 标题 undefined undefined在大多数情况下,它们是相互作用的
- 改变property,通过attribute获取的值,会随着改变;
- 通过attribute操作修改,property的值会随着改变;
- 但是input的value修改只能通过attribute的方法;
除非特别情况,大多数情况下,设置、获取attribute,推荐使用property的方式:
这是因为它默认情况下是有类型的;
javascript
// input元素
var inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
// if (inputEl.getAttribute("checked")) {
// console.log("checkbox处于选中状态")
// }
if (inputEl.checked) { // true
console.log("checkbox处于选中状态")
}
console.log(typeof inputEl.checked) // boolean
// 2.attribute和property是相互影响的
boxEl.id = "aaaaa"
console.log(boxEl.getAttribute("id"))
boxEl.setAttribute("title", "哈哈哈")
console.log(boxEl.title)
// 3.比较特殊的情况, input设置值(了解)
var accountInputEl = document.querySelector(".account")
var btnEl = document.querySelector(".btn")
btnEl.onclick = function() {
accountInputEl.setAttribute("value", "kobe")
// 优先级更高
accountInputEl.value = "coderwhy"
}JavaScript动态修改样式
有时候我们会通过JavaScript来动态修改样式,这个时候我们有两个选择:
- 选择一:在CSS中编写好对应的样式,动态的添加class;
- 选择二:动态的修改style属性;
开发中如何选择呢?
在大多数情况下,如果可以动态修改class完成某个功能,更推荐使用动态class;
如果对于某些情况,无法通过动态修改class(比如精准修改某个css属性的值),那么就可以修改style属性;
html
<div class="box">
我是box
</div>如果想将box字体改为红色,大小改为24px,背景为绿色,一种做法是直接修改style
javascript
// 1.获取boxEl
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 2.监听点击
boxEl.onclick = function() {
// 1.直接修改style
boxEl.style.color = "red"
boxEl.style.fontSize = "24px"
boxEl.style.backgroundColor = "green"
}但是这种做法不好维护,可以采用添加class的方法
javascript
// 1.获取boxEl
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 2.监听点击
boxEl.onclick = function() {
// 2.动态的添加某一个class
boxEl.className = "active"
}css
.active {
color: red;
font-size: 24px;
background-color: green;
}如果想要精准的修改css属性的值,那么得使用style,动态添加的class样式是写死的,没法改
javascript
// 1.获取boxEl
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 2.监听点击
var counter = 1
boxEl.onclick = function() {
// 3.动态的修改boxEl的宽度,每点击一次宽度加100px
boxEl.style.width = 100 * counter + "px"
counter++
}元素的className和classList
html
<div class="box">
我是box
</div>元素的class attribute,对应的property并非叫class,而是className:
- 这是因为JavaScript早期是不允许使用class这种关键字来作为对象的属性,所以DOM规范使用了className;
- 虽然现在JavaScript已经没有这样的限制,但是并不推荐,并且依然在使用className这个名称;
我们可以对className进行赋值,它会替换整个类中的字符串。
javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 1.方法一: className
boxEl.className = "abc" // class会替换成abc如果我们需要添加或者移除单个的class,那么可以使用classList属性。
elem.classList 是一个特殊的对象:
- elem.classList.add (class) :添加一个类
- elem.classList.remove(class):添加/移除类。
- elem.classList.toggle(class) :如果类不存在就添加类,存在就移除它。
- elem.classList.contains(class):检查给定类,返回 true/false。
classList是可迭代对象,可以通过for of进行遍历。
html
<div class="box">
我是box
</div>
<button class="btn">切换</button>css
.active {
color: #fff;
background-color: #f80;
font-size: 25px;
}javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 2.方法二: classList操作class
boxEl.classList.add("abc")
boxEl.classList.add("active")
boxEl.classList.remove("abc")
// 需求: box在active之间切换
var btnEl = document.querySelector(".btn")
btnEl.onclick = function() {
// 方法一:
// if (boxEl.classList.contains("active")) {
// boxEl.classList.remove("active")
// } else {
// boxEl.classList.add("active")
// }
// 方法二:
boxEl.classList.toggle("active")
}元素的style属性
html
<div class="box" style="background-color: aqua; color: white;">
我是box
</div>如果需要单独修改某一个CSS属性,那么可以通过style来操作:
对于多词(multi-word)属性,使用驼峰式 camelCase
javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 1.在property中使用的驼峰格式
console.log(boxEl.style.backgroundColor)如果我们将值设置为空字符串,那么会使用CSS的默认样式:
javascript
// 2.如果将一个属性的值, 设置为空的字符串, 那么是使用默认值
boxEl.style.display = ""
boxEl.style.fontSize = ""多个样式的写法,我们需要使用cssText属性:
不推荐这种用法,因为它会替换整个字符串;
javascript
// 3.设置多个样式
// boxEl.style.fontSize = "30px"
// boxEl.style.color = "red"
boxEl.style.cssText = "font-size: 30px; color: red;"元素style的读取 - getComputedStyle
html
<div class="box" style="background-color: red;">
我是box
</div>css
.box {
font-size: 20px;
}如果我们需要读取样式:
- 对于内联样式,是可以通过style.*的方式读取到的;
- 对于style、css文件中的样式,是读取不到的;
javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
console.log(boxEl.style.backgroundColor) // 可以读取到
console.log(boxEl.style.fontSize) // 读取不到这个时候,我们可以通过getComputedStyle的全局函数来实现:
javascript
console.log(getComputedStyle(boxEl).fontSize)HTML5的data-*自定义属性
前面我们有学习HTML5的data-*自定义属性,那么它们也是可以在dataset属性中获取到的:
HTML
<div id="abc" class="box"
data-age="18" data-height="1.88"></div>javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 小程序开发中使用
console.log(boxEl.dataset.age)
console.log(boxEl.dataset.height)创建元素
前面我们使用过 document.write 方法写入一个元素:
- 这种方式写起来非常便捷,但是对于复杂的内容、元素关系拼接并不方便;
- 它是在早期没有DOM的时候使用的方案,目前依然被保留了下来;
那么目前我们想要插入一个元素,通常会按照如下步骤:
- 步骤一:创建一个元素;
- 步骤二:插入元素到DOM的某一个位置;
创建元素: document.createElement(tag)
javascript
// 1.通过innerHTML(不推荐)
// boxEl.innerHTML = `
// <h2 class="title">我是标题</h2>
// `
// 2.真实创建一个DOM对象
var h2El = document.createElement("h2")
h2El.className = "title"
h2El.classList.add("active")
h2El.textContent = "我是标题"插入元素
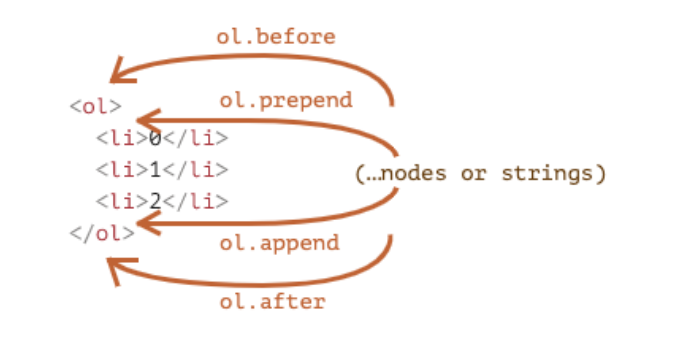
插入元素的方式如下:
- node.append(...nodes or strings) —— 在 node 末尾 插入节点或字符串
- node.prepend(...nodes or strings) —— 在 node 开头 插入节点或字符串
- node.before(...nodes or strings) —— 在 node 前面 插入节点或字符串
- node.after(...nodes or strings) —— 在 node 后面 插入节点或字符串
- node.replaceWith(...nodes or strings) —— 将 node 替换为给定的节点或字符串
html
<span>111111</span>
<div class="box">
<span class="box-first">呵呵呵呵</span>
<p>哈哈哈哈哈</p>
</div>javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 插入到span和p元素之间
// var spanEl = document.querySelector("span")
// var spanEl = boxEl.children[0]
var spanEl = boxEl.querySelector("span")
spanEl.after(h2El)移除和克隆元素
移除元素我们可以调用元素本身的remove方法:
html
<button class="remove-btn">移除box</button>
<div class="box">
<h2>我是标题</h2>
<p>我是文本, 哈哈哈哈哈</p>
</div>javascript
// 1.获取元素
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
var removeBtnEl = document.querySelector(".remove-btn")
// 2.监听removeBtn的点击
removeBtnEl.onclick = function() {
boxEl.remove()
}如果我们想要复制一个现有的元素,可以通过cloneNode方法:
- 可以传入一个Boolean类型的值,来决定是否是深度克隆;
- 深度克隆会克隆对应元素的子元素,否则不会
html
<button class="clone-btn">复制box</button>
<div class="box">
<h2>我是标题</h2>
<p>我是文本, 哈哈哈哈哈</p>
</div>javascript
// 1.获取元素
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
var cloneBtnEl = document.querySelector(".clone-btn")javascript
// 3.复制box
var counter = 0
cloneBtnEl.onclick = function() {
var newNode = boxEl.cloneNode(true)
newNode.children[0].textContent = "我是标题" + counter
// boxEl.after(newNode)
document.body.append(newNode)
counter++
}旧的元素操作方法(了解)
在很多地方我们也会看到一些旧的操作方法:
parentElem.appendChild(node):在parentElem的父元素最后位置添加一个子元素
parentElem.insertBefore(node, nextSibling):在parentElem的nextSibling前面插入一个子元素
parentElem.replaceChild(node, oldChild):在parentElem中,新元素替换之前的oldChild元素
parentElem.removeChild(node):在parentElem中,移除某一个元素
全局变量的使用细节
点击+按钮加1,点击-按钮减1
html
<button class="add">+</button>
<button class="sub">-</button>
<h2 class="counter">0</h2>javascript
// 1.获取按钮
var addEl = document.querySelector(".add")
var subEl = document.querySelector(".sub")
var h2El = document.querySelector(".counter")
// 2.监听btnEl的点击
var counter = 0
addEl.onclick = function() {
counter++
h2El.textContent = counter
}
subEl.onclick = function() {
counter--
h2El.textContent = counter
}元素的大小、滚动
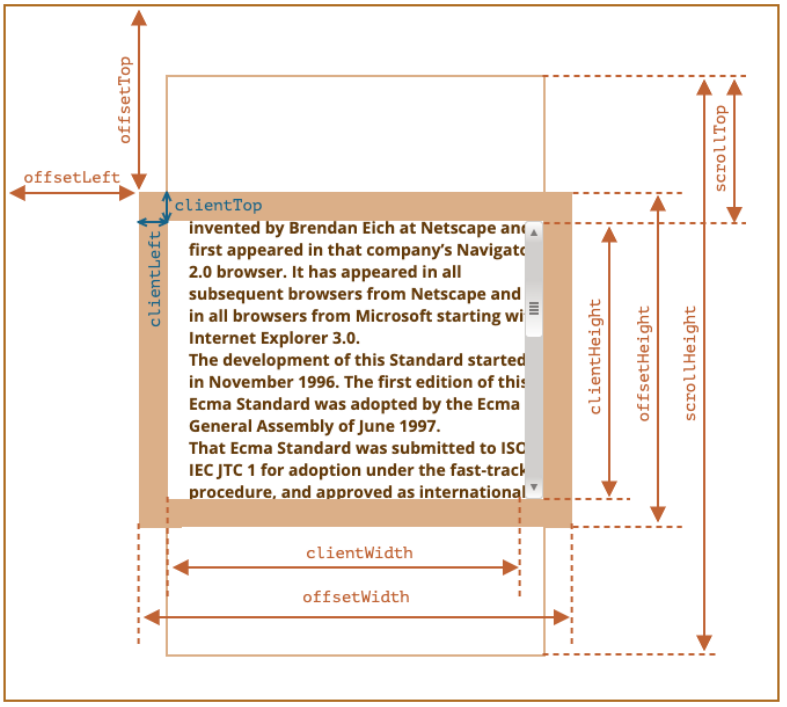
clientWidth:contentWith+padding(不包含滚动条)
clientHeight:contentHeight+padding
clientTop:border-top的宽度
clientLeft:border-left的宽度
offsetWidth:元素完整的宽度
offsetHeight:元素完整的高度
offsetLeft:距离父元素的x
offsetHeight:距离父元素的y
scrollHeight:整个可滚动的区域高度
scrollTop:滚动部分的高度
html
<div class="box">
你去过国内最美的地方是哪# 我去过国内最美的地方是新疆喀纳斯。喀纳斯是一个美丽而神秘的地方,这里群山环抱,森林密布,湖水清澈,风景奇特。为国家级5A级景区,国家地质公园,国家森林公园。
</div>css
body {
padding: 100px;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* box-sizing: border-box; */
background-color: orange;
overflow: auto;
}javascript
var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
// 1.获取样式(局限性很强)
// var boxStyle = getComputedStyle(boxEl)
// console.log(boxStyle.width, boxStyle.height)
// 2.获取更多信息
console.log(boxEl.clientWidth)
console.log(boxEl.clientHeight)
console.log(boxEl.clientLeft)
console.log(boxEl.clientTop)
console.log(boxEl.offsetWidth)
console.log(boxEl.offsetHeight)
console.log(boxEl.offsetLeft)
console.log(boxEl.offsetTop)
console.log(boxEl.scrollHeight)
console.log(boxEl.scrollTop)
// window对象
window.onclick = function() {
console.log(boxEl.scrollTop) // 先滚动,然后点击window获取滚动的距离
}window的大小、滚动
window的width和height
innerWidth、innerHeight:获取window窗口的宽度和高度(包含滚动条)
outerWidth、outerHeight:获取window窗口的整个宽度和高度(包括调试工具、工具栏)
documentElement.clientHeight、documentElement.clientWidth:获取html的宽度和高度(不包含滚动条)
javascript
// window大小
console.log(window.outerWidth)
console.log(window.outerHeight)
console.log(window.innerWidth)
console.log(window.innerHeight)
console.log(document.documentElement.offsetWidth)
console.log(document.documentElement.offsetHeight)window的滚动位置:
scrollX:X轴滚动的位置(别名pageXOffset)
scrollY:Y轴滚动的位置(别名pageYOffset)
javascript
// 获取window的滚动区域
window.onclick = function() {
console.log(window.scrollX)
console.log(window.scrollY)
}也有提供对应的滚动方法:
方法 scrollBy(x,y) :将页面滚动至 相对于当前位置的 (x, y) 位置
方法 scrollTo(pageX,pageY) 将页面滚动至 绝对坐标
javascript
scrollBtnEl.onclick = function() {
window.scrollBy(0, 100) // 在原先基础上增加100,每次点击y都会增加100
}下面来完成一个需求,当滚动y方向的距离超过600时,显示回到顶部按钮,否则隐藏该按钮。
加很多br是为了让y方向有滚动条
html
<div class="box"></div>
<button class="scroll-btn">回到顶部</button>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>方法一:
使用display来控制显示和隐藏
css
.scroll-btn {
position: fixed;
right: 20px;
bottom: 20px;
display: none; // 开始先隐藏
}javascript
var scrollBtnEl = document.querySelector(".scroll-btn")
window.onscroll = function() {
var scrollY = window.scrollY
if (scrollY > 600) {
scrollBtnEl.style.display = "block"
} else {
scrollBtnEl.style.display = "none"
}
}
// 点击按钮后滚动到某个位置
scrollBtnEl.onclick = function() {
window.scrollTo(0, 0) // 回到顶部
}方法二:
使用hidden来控制显示和隐藏
css
.scroll-btn {
position: fixed;
right: 20px;
bottom: 20px;
}javascript
var scrollBtnEl = document.querySelector(".scroll-btn")
scrollBtnEl.hidden = true // 开始先隐藏
window.onscroll = function() {
var scrollY = window.scrollY
if (scrollY > 600) {
scrollBtnEl.hidden = false
} else {
scrollBtnEl.hidden = true
}
}
// 点击按钮后滚动到某个位置
scrollBtnEl.onclick = function() {
window.scrollTo(0, 0)
}案例的练习-动态输入列表
一直往ul中插入li,直到输入为空停止
html
<h1>动态创建列表</h1>
<ul class="list"></ul>javascript
var ulEl = document.querySelector(".list")
var isFlag = true
while (isFlag) {
var message = prompt("请输入信息:")
if (!message) { // 没有输入内容
isFlag = false
} else {
var liEl = document.createElement("li")
liEl.textContent = message
ulEl.append(liEl)
}
}案例的练习-动态显示时间
html
<h1 class="time">2022-05-19 11:14:30</h1>javascript
// 封装了工具函数
// 对月份那些进行转换,比如1月转成01,count是传入的位数,不传默认是2位,padStr表示用什么补齐
function padLeft(content, count, padStr) {
count = count || 2
padStr = padStr || "0"
content = String(content)
return content.padStart(count, padStr)
}
// 1.获取时间的元素
var timeEl = document.querySelector(".time")
setInterval(function() {
// 2.获取具体的时间并且进行格式化
var date = new Date()
var year = date.getFullYear()
var month = padLeft(date.getMonth() + 1)
var day = padLeft(date.getDate())
var hour = padLeft(date.getHours())
var minute = padLeft(date.getMinutes())
var second = padLeft(date.getSeconds())
// 3.将时间放到timeEl中
timeEl.textContent = `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${minute}:${second}`
}, 1000);案例练习-倒计时的显示
html
<div class="countdown">
<span class="time hour">03</span>
<span class="split">:</span>
<span class="time minute">25</span>
<span class="split">:</span>
<span class="time second">43</span>
</div>css
.countdown {
color: #f00;
font-size: 20px;
}
.countdown .time {
background-color: #f00;
color: #fff;
display: inline-block;
padding: 5px;
border-radius: 3px;
}javascript
// 封装了工具函数
function formatPadLeft(content, count, padStr) {
count = count || 2
padStr = padStr || "0"
content = String(content)
return content.padStart(count, padStr)
}
// 1.获取元素
var hourEl = document.querySelector(".hour")
var minuteEl = document.querySelector(".minute")
var secondEl = document.querySelector(".second")
var endDate = new Date()
endDate.setHours(24)
endDate.setMinutes(0)
endDate.setSeconds(0)
endDate.setMilliseconds(0)
setInterval(function() {
// 获取倒计时的小时-分钟-秒钟
// 11:53:22 => 24:00:00
var nowDate = new Date()
var intervalTime = Math.floor((endDate.getTime() - nowDate.getTime()) / 1000)
// console.log(intervalTime)
// 43324: x小时x分钟x秒钟
var hour = Math.floor(intervalTime / 3600)
var minute = Math.floor(intervalTime / 60) % 60
var second = intervalTime % 60
// 2.设置内容
hourEl.textContent = formatPadLeft(hour)
minuteEl.textContent = formatPadLeft(minute)
secondEl.textContent = formatPadLeft(second)
}, 1000)