Appearance
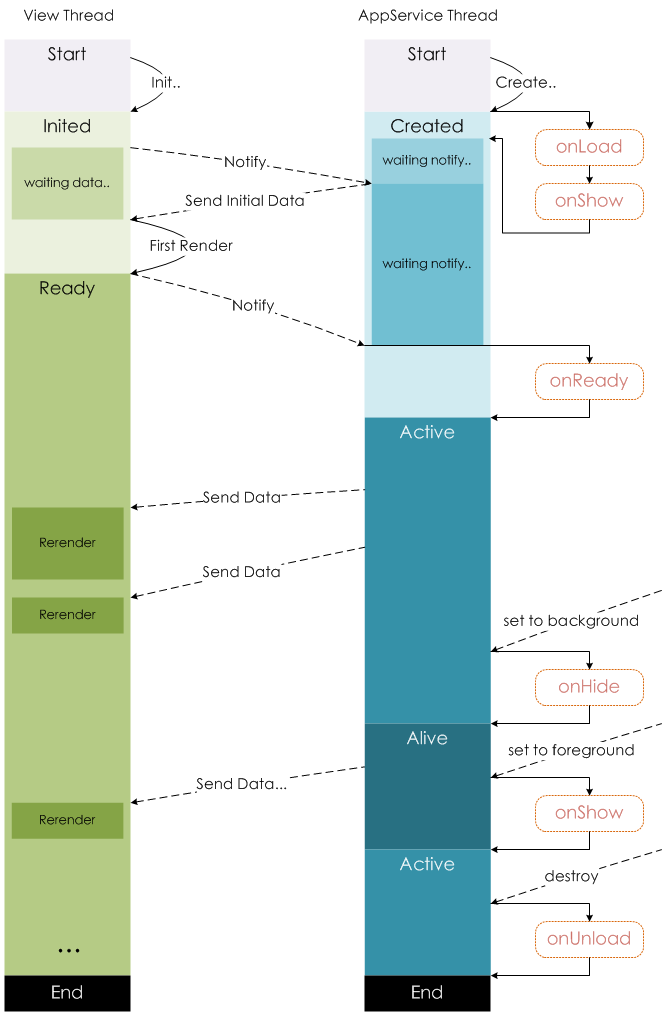
小程序的架构模型
谁是小程序的宿主环境呢?微信客户端
宿主环境为了执行小程序的各种文件:wxml文件、wxss文件、js文件
当小程序基于WebView环境下时,WebView的 JS逻辑、DOM树创建、CSS解析、样式计算、Layout、Paint (Composite)都发生
在同一线程,在 WebView 上执行过多的 JS 逻辑可能阻塞渲染,导致界面卡顿。
以此为前提,小程序同时考虑了性能与安全,采用了目前称为「双线程模型」的架构。
双线程模型:
WXML模块和WXSS样式运行于 渲染层,渲染层使用WebView线程渲染(一个程序有多个页面,会使用多个WebView的线程)。
JS脚本(app.js/home.js等)运行于 逻辑层,逻辑层使用JsCore运行JS脚本。
这两个线程都会经由微信客户端(Native)进行中转交互。
小程序的配置文件
小程序的很多开发需求被规定在了配置文件中。
为什么这样做呢?
这样做可以更有利于我们的开发效率;
并且可以保证开发出来的小程序的某些风格是比较一致的;
比如导航栏 – 顶部TabBar,以及页面路由等等。
常见的配置文件有哪些呢?
project.config.json:项目配置文件, 比如项目名称、appid等;
我们一般不会去改动这个文件,如果需要改的话,在详情=>本地设置进行修改,修改完会自动同步到这个文件中
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/devtools/projectconfig.html
sitemap.json:小程序搜索相关的;
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/framework/sitemap.html
app.json:全局配置;
page.json:页面配置;
全局app配置文件
全局配置比较多, 我们这里将几个比较重要的. 完整的查看官方文档.
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/reference/configuration/app.html
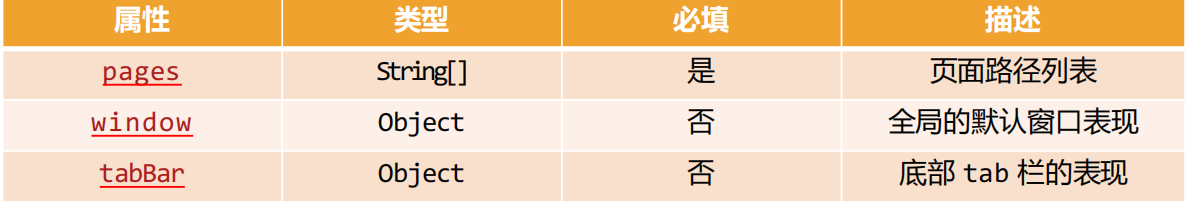
pages: 页面路径列表
用于指定小程序由哪些页面组成,每一项都对应一个页面的 路径(含文件名) 信息。
小程序中所有的页面都是必须在pages中进行注册的。
window: 全局的默认窗口展示
用户指定窗口如何展示, 其中还包含了很多其他的属性
其中backgroundTextStyle是下拉 loading 的样式,仅支持 dark / light,但是默认是不开启下拉刷新的,如果想要开启下来刷新,需要来到页面,比如favor页面的favor.json文件开启下拉刷新
pages/favor/favor.json
json
{
"usingComponents": {},
"enablePullDownRefresh": true // 开启下拉刷新
}tabBar: 顶部tab栏的展示
具体属性稍后我们进行演示
配置案例实现
app.json
json
{
"pages": [
"pages/index/index",
"pages/favor/favor",
"pages/order/order",
"pages/profile/profile",
"pages/01test/index"
],
"window": {
"backgroundTextStyle": "dark",
"navigationBarBackgroundColor": "#ff8189",
"navigationBarTitleText": "弘源旅途",
"navigationBarTextStyle": "white"
},
"tabBar": {
"selectedColor": "#ff8189",
"list": [
{
"text": "首页",
"pagePath": "pages/index/index",
"iconPath": "assets/tabbar/home.png",
"selectedIconPath": "assets/tabbar/home_active.png"
},
{
"text": "收藏",
"pagePath": "pages/favor/favor",
"iconPath": "assets/tabbar/category.png",
"selectedIconPath": "assets/tabbar/category_active.png"
},
{
"text": "订单",
"pagePath": "pages/order/order",
"iconPath": "assets/tabbar/cart.png",
"selectedIconPath": "assets/tabbar/cart_active.png"
},
{
"text": "我的",
"pagePath": "pages/profile/profile",
"iconPath": "assets/tabbar/profile.png",
"selectedIconPath": "assets/tabbar/profile_active.png"
}
]
},
"style": "v2",
"sitemapLocation": "sitemap.json"
}页面page配置文件
每一个小程序页面也可以使用 .json 文件来对本页面的窗口表现进行配置。
页面中配置项在当前页面会覆盖 app.json 的 window 中相同的配置项。
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/reference/configuration/page.html
pages/profile/profile.json
json
{
"usingComponents": {}, // 使用组件要在这里注册
"navigationBarTitleText": "个人信息",
"navigationBarBackgroundColor": "#f00",
"enablePullDownRefresh": true, // 开启下拉刷新
"onReachBottomDistance": 100 // 距离底部100就加载更多数据,默认是0
}pages/profile/profile.js
javascript
// pages/profile/profile.js
Page({
data: {
avatarURL: "",
listCount: 30
},
// 监听下拉刷新
onPullDownRefresh() {
console.log("用户进行下拉刷新~");
// 模拟网络请求: 定时器
setTimeout(() => {
this.setData({ listCount: 30 })
// API: 停止下拉刷新
wx.stopPullDownRefresh({
success: (res) => {
console.log("成功停止了下拉刷新", res);
},
fail: (err) => {
console.log("失败停止了下拉刷新", err);
}
})
}, 1000)
},
// 监听页面滚动到底部
onReachBottom() {
console.log("onReachBottom");
this.setData({
listCount: this.data.listCount + 30
})
}
})注册小程序 – App函数
每个小程序都需要在 app.js 中调用 App 函数注册小程序实例
在注册时, 可以绑定对应的生命周期函数;
在生命周期函数中, 执行对应的代码;
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/reference/api/App.html
我们来思考:注册App时,我们一般会做什么呢?
1.判断小程序的进入场景
2.监听生命周期函数,在生命周期中执行对应的业务逻辑,比如在某个生命周期函数中进行登录操作或者请求网络数据;
3.因为App()实例只有一个,并且是全局共享的(单例对象),所以我们可以将一些共享数据放在这里;
作用一:判断打开场景
小程序的打开场景较多:
常见的打开场景:群聊会话中打开、小程序列表中打开、微信扫一扫打开、另一个小程序打开
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/reference/scene-list.html
如何确定场景?
在onLaunch和onShow生命周期回调函数中,会有options参数,其中有scene值;
app.js
onLaunch只会执行一次,而onShow会执行多次
javascript
App({
onShow(options) {
// 作用一: 判断小程序的进入场景
console.log("onShow:", options);
},
})作用二:定义全局App的数据
作用二:可以在Object中定义全局App的数据
定义的数据可以在其他任何页面中访问:
app.js
javascript
App({
// 作用二: 共享数据
// 数据不是响应式, 这里共享的数据通常是一些固定的数据
globalData: {
token: "",
userInfo: {}
},
})pages/order/order.js
javascript
// pages/order/order.js
Page({
data: {
userInfo: {}
},
onLoad() {
// 获取共享的数据: App实例中数据
// 1.获取app实例对象
const app = getApp()
// 2.从app实例对象获取数据
const token = app.globalData.token
const userInfo = app.globalData.userInfo
console.log(token, userInfo);
// 3.拿到token目的发送网络请求
// 4.将数据展示到界面上面
// this.data.userInfo = userInfo
this.setData({ userInfo })
console.log(this.data.userInfo);
}
})pages/order/order.wxml
html
<!--pages/order/order.wxml-->
<text>pages/order/order.wxml</text>
<view class="user">
<view class="name">name: {{ userInfo.nickname }}</view>
<view class="level">level: {{ userInfo.level }}</view>
</view>作用三 – 生命周期函数
作用三:在生命周期函数中,完成应用程序启动后的初始化操作
比如登录操作(这个后续会详细讲解);
比如读取本地数据(类似于token,然后保存在全局方便使用)
比如请求整个应用程序需要的数据;
app.js
javascript
App({
globalData: {
token: "",
userInfo: {}
},
onLaunch(options) {
// 0.从本地获取token/userInfo
const token = wx.getStorageSync("token")
const userInfo = wx.getStorageSync("userInfo")
// 1.进行登录操作(判断逻辑)
if (!token || !userInfo) {
// 将登录成功的数据, 保存到storage
console.log("登录操作");
wx.setStorageSync("token", "kobetoken")
wx.setStorageSync("userInfo", { nickname: "kobe", level: 100 })
}
// 2.将获取到数据保存到globalData中
this.globalData.token = token
this.globalData.userInfo = userInfo
// 3.发送网络请求, 优先请求一些必要的数据
// wx.request({ url: 'url'})
},
})注册页面 – Page函数
小程序中的每个页面, 都有一个对应的js文件, 其中调用Page函数注册页面示例
在注册时, 可以绑定初始化数据、生命周期回调、事件处理函数等。
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/reference/api/Page.html
我们来思考:注册一个Page页面时,我们一般需要做什么呢?
1.在生命周期函数中发送网络请求,从服务器获取数据;
2.初始化一些数据,以方便被wxml引用展示;
3.监听wxml中的事件,绑定对应的事件函数;
4.其他一些监听(比如页面滚动、上拉刷新、下拉加载更多等);
html
<!--pages/01_初体验/index.wxml-->
<view class="banner">
<swiper circular autoplay indicator-dots="{{true}}">
<block wx:for="{{banners}}" wx:key="acm">
<swiper-item>
<!-- image组件默认宽度和高度: 320x240 -->
<image mode="widthFix" src="{{item.image}}"></image>
</swiper-item>
</block>
</swiper>
</view>
<view class="counter">
<view>当前计数: {{ counter }}</view>
</view>
<view class="buttons">
<button bindtap="onBtn1Click">按钮1</button>
<block wx:for="{{btns}}" wx:key="*this">
<button
class="btn"
style="background: {{item}};"
bindtap="onBtnClick"
data-color="{{item}}"
>
{{ item }}
</button>
</block>
</view>
<view class="list">
<block wx:for="{{30}}" wx:key="*this">
<view>列表数据:{{ item }}</view>
</block>
</view>javascript
// pages/01_初体验/index.js
Page({
data: {
banners: [],
recommends: [],
// 2.作用二: 定义本地固定的数据
counter: 100,
btns: ["red", "blue", "green", "orange"]
},
// 1.作用一: 发送网络请求, 请求数据
onLoad() {
console.log("onLoad");
// 发送网络请求
wx.request({
url: "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata",
success: (res) => {
const data = res.data.data
const banners = data.banner.list
const recommends = data.recommend.list
this.setData({ banners, recommends })
}
})
},
// 3.绑定wxml中产生事件后的回调函数
onBtn1Click() {
console.log("onBtn1Click");
},
onBtnClick(event) {
console.log("btn click:", event.target.dataset.color);
},
// 4.绑定下拉刷新/达到底部/页面滚动
onPullDownRefresh() {
console.log("onPullDownRefresh");
},
onReachBottom() {
console.log("onReachBottom");
},
onPageScroll(event) { // 页面滚动
console.log("onPageScroll:", event);
},
// 生命周期函数:
onShow() {
console.log("onShow");
},
onReady() {
console.log("onReady");
},
onHide() {
console.log("onHide");
},
onUnload() {
console.log("onUnload");
}
})Page页面的生命周期