Appearance
认识Plugin
Webpack的另一个核心是Plugin,官方有这样一段对Plugin的描述:
While loaders are used to transform certain types of modules, plugins can be leveraged to perform a wider range
of tasks like bundle optimization, asset management and injection of environment variables.
上面表达的含义翻译过来就是:
Loader是用于特定的模块类型进行转换;
Plugin可以用于执行更加广泛的任务,比如打包优化、资源管理、环境变量注入等;
CleanWebpackPlugin
前面我们演示的过程中,每次修改了一些配置,重新打包时,都需要手动删除dist文件夹:
我们可以借助于一个插件来帮助我们完成,这个插件就是CleanWebpackPlugin;
首先,我们先安装这个插件:
npm install clean-webpack-plugin -D
之后在插件中配置:
javascript
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require("clean-webpack-plugin")
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
]
}除了使用CleanWebpackPlugin插件,也可以直接在output中配置clean,效果一样
javascript
module.exports = {
mode: "production",
entry: "./src/main.js",
output: {
filename: "bundle.js",
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "./build"),
clean: true // 同CleanWebpackPlugin插件
}
}HtmlWebpackPlugin
另外还有一个不太规范的地方:
我们的HTML文件是编写在根目录下的,而最终打包的dist文件夹中是没有index.html文件的。
在进行项目部署的时,必然也是需要有对应的入口文件index.html;
所以我们也需要对index.html进行打包处理;
对HTML进行打包处理我们可以使用另外一个插件:HtmlWebpackPlugin;
npm install html-webpack-plugin -D
javascript
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin()
]
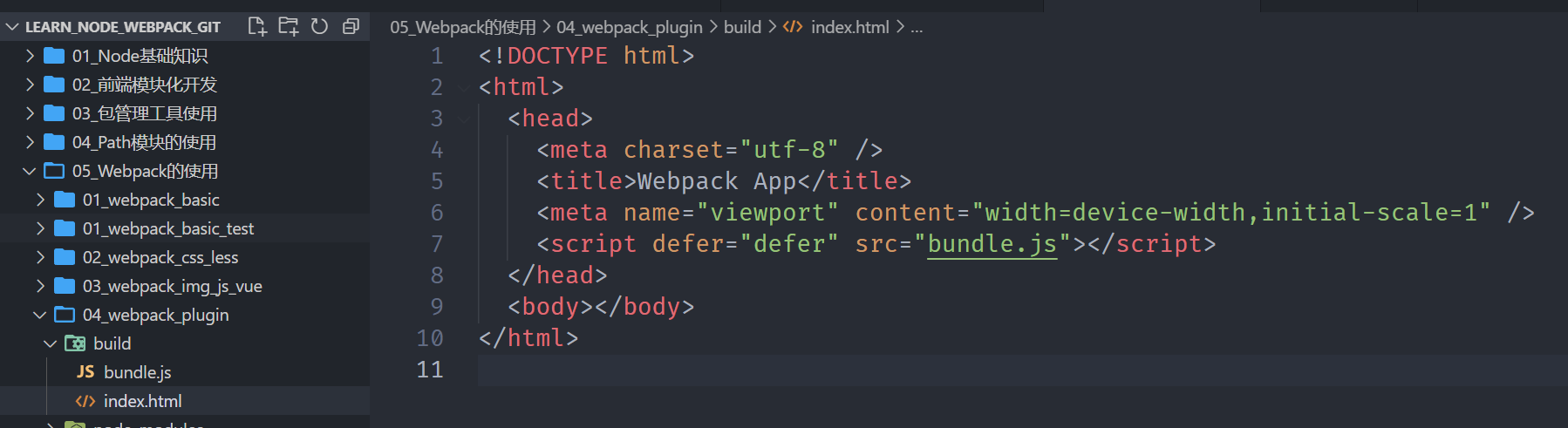
}重新打包之后,就会在打包的文件夹下面生成一个index.html
生成index.html分析
我们会发现,现在自动在dist文件夹中,生成了一个index.html的文件:
该文件中也自动添加了我们打包的bundle.js文件;
如果我们想改index.html文件中的title,可以在HtmlWebpackPlugin中传参
javascript
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: "电商项目",
})这个文件是如何生成的呢?
默认情况下是根据ejs的一个模板来生成的;
在html-webpack-plugin的源码中,有一个default_index.ejs模块;
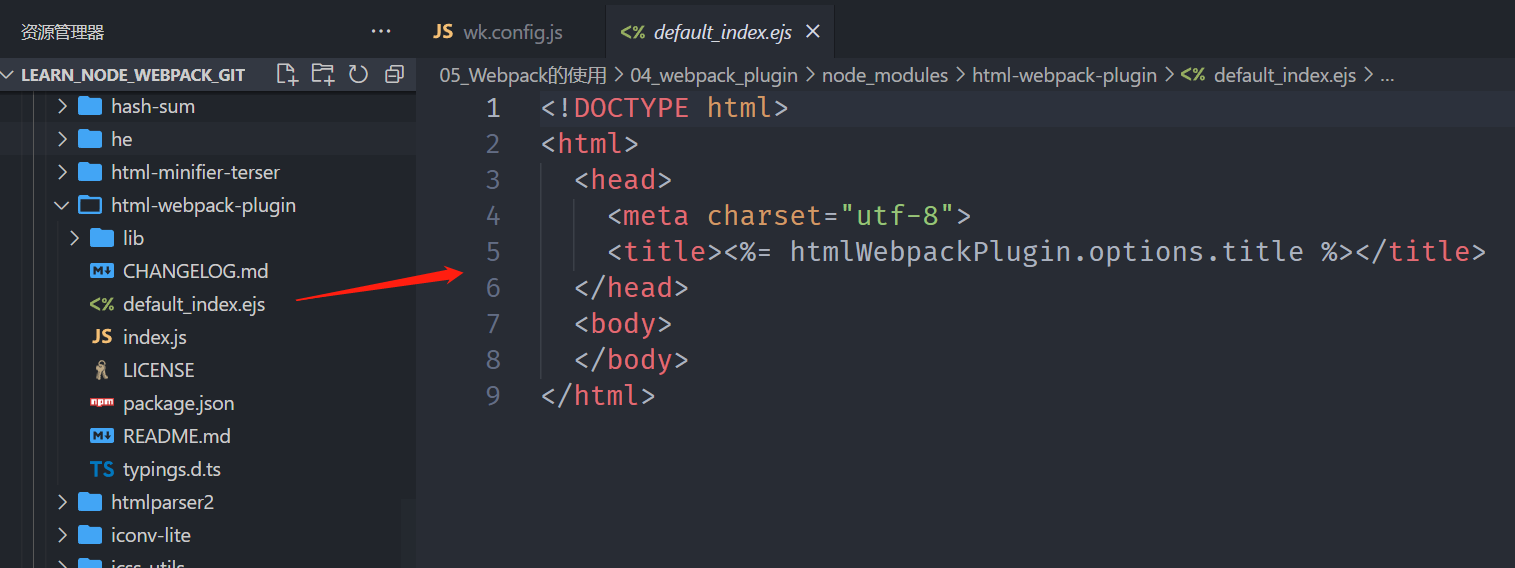
自定义HTML模板
如果我们想在自己的模块中加入一些比较特别的内容:
比如添加一个noscript标签,在用户的JavaScript被关闭时,给予响应的提示;
比如在开发vue或者react项目时,我们需要一个可以挂载后续组件的根标签
;这个我们需要一个属于自己的index.html模块:
这里将index.html事先准备好
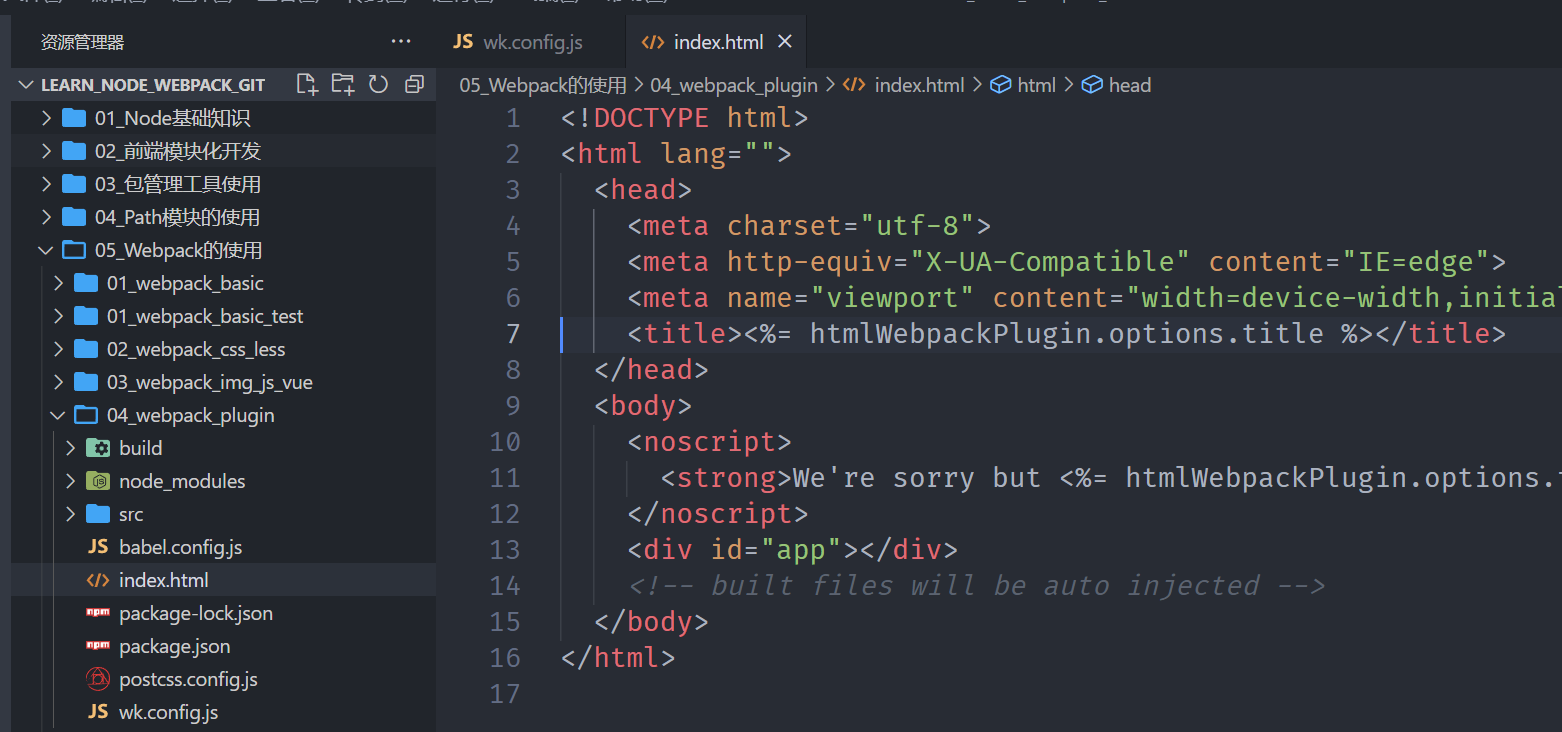
index.html
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>然后,在插件中使用自定义的模板,打包后的index.html就会使用这个模板
javascript
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: "电商项目",
template: "./index.html"
})自定义模板数据填充
上面的代码中,会有一些类似这样的语法<% 变量 %>,这个是EJS模块填充数据的方式。
在配置HtmlWebpackPlugin时,我们可以添加如下配置:
**template:**指定我们要使用的模块所在的路径;
**title:**在进行htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title读取时,就会读到该信息;
DefinePlugin的介绍
但是,这个时候编译还是会报错,因为在我们的模块中还使用到一个BASE_URL的常量:
这是因为在编译template模块时,有一个BASE_URL:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico"> // 这里有BASE_URL,刚才演示HtmlWebpackPlugin时候先将这里删除,因为BASE_URL必须使用DefinePlugin插件
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>html
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">但是我们并没有设置过这个常量值,所以会出现没有定义的错误;
这个时候我们可以使用DefinePlugin插件;
DefinePlugin的使用
DefinePlugin允许在编译时创建配置的全局常量,是一个webpack内置的插件(不需要单独安装):
这个时候,编译template就可以正确的编译了,会读取到BASE_URL的值;
javascript
const { DefinePlugin } = require("webpack")
plugins: [
new DefinePlugin({
BASE_URL: "'./'"
})
]打包后的index.html中的BASE_URL也被解析成./
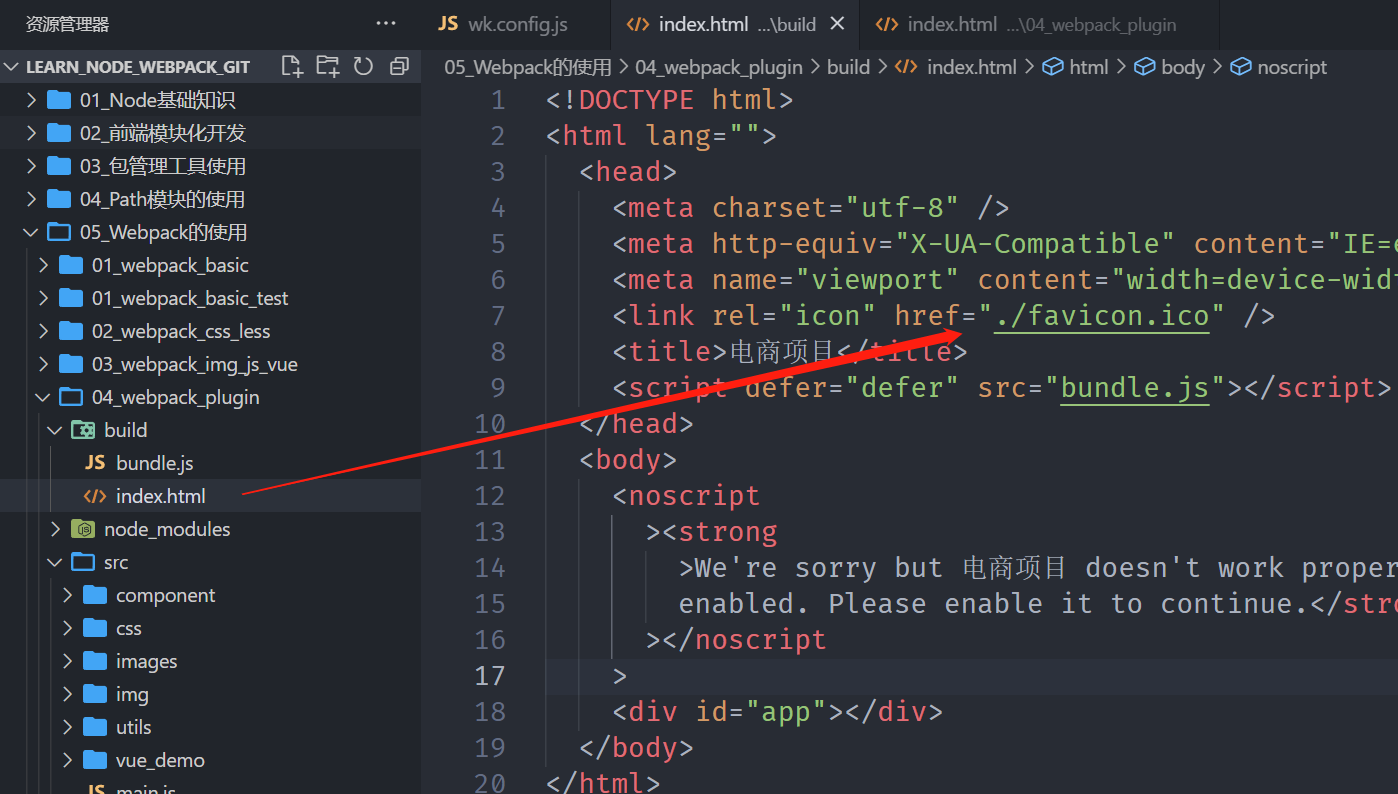
当然,我们也可以定义一些全局变量,在项目任何地方都能使用
javascript
plugins: [
new DefinePlugin({
BASE_URL: "'./'",
coderwhy: "'why'",
counter: "123"
})
]在main.js中使用
javascript
// 使用通过DefinePlugin注入的变量
console.log(coderwhy) // why
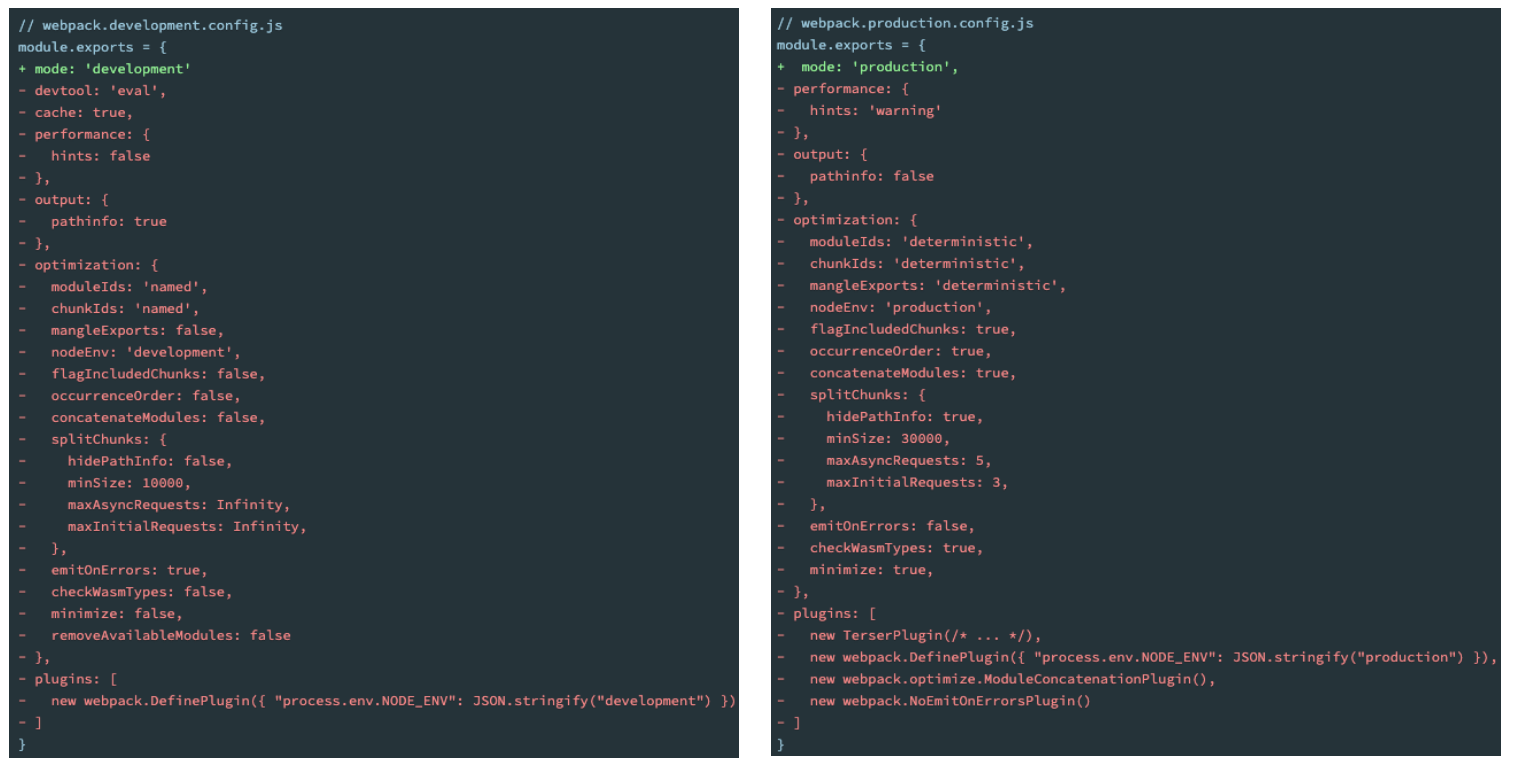
console.log(counter) // 123Mode配置
前面我们一直没有讲mode。
Mode配置选项,可以告知webpack使用相应模式的内置优化:
默认值是production(什么都不设置的情况下);
可选值有:'none' | 'development' | 'production';
这几个选项有什么样的区别呢?
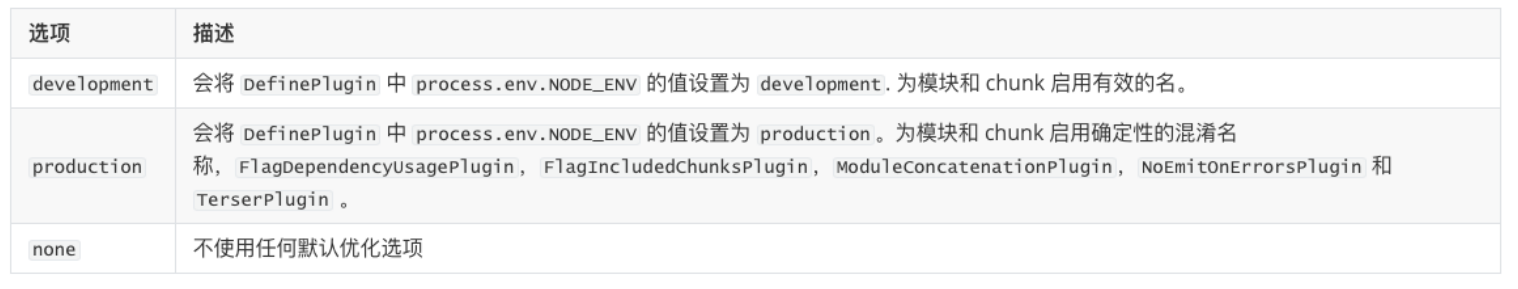
Mode配置代表更多
配置了mode为development或production,相当于分别配置了对应底下的红色部门。