Appearance
Webpack和Tapable
我们知道webpack有两个非常重要的类:Compiler和Compilation
他们通过注入插件的方式,来监听webpack的所有生命周期;
插件的注入离不开各种各样的Hook,而他们的Hook是如何得到的呢?
其实是创建了Tapable库中的各种Hook的实例;
所以,如果我们想要学习自定义插件,最好先了解一个库:Tapable
Tapable是官方编写和维护的一个库;
Tapable是管理着需要的Hook,这些Hook可以被应用到我们的插件中;
Tapable有哪些Hook呢?
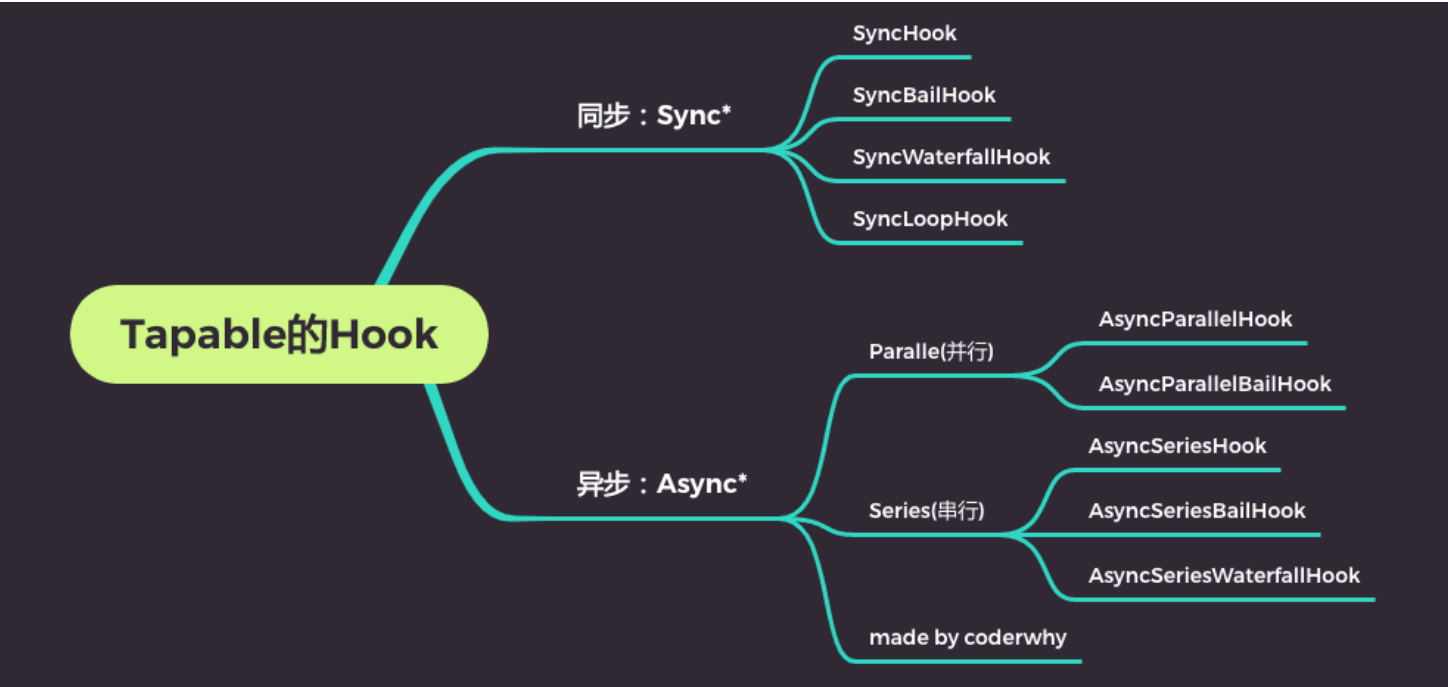
Tapable的Hook分类
同步和异步的:
以sync开头的,是同步的Hook;
以async开头的,两个事件处理回调,不会等待上一次处理回调结束后再执行下一次回调;
其他的类别
- bail:当有返回值时,就不会执行后续的事件触发了;
- Loop:当返回值为true,就会反复执行该事件,当返回值为undefined或者不返回内容,就退出事件;
- Waterfall:当返回值不为undefined时,会将这次返回的结果作为下次事件的第一个参数;
- Parallel:并行,会同时执行次事件处理回调结束,才执行下一次事件处理回调;
- Series:串行,会等待上一是异步的Hook;
Hook的使用过程
第一步:创建Hook对象
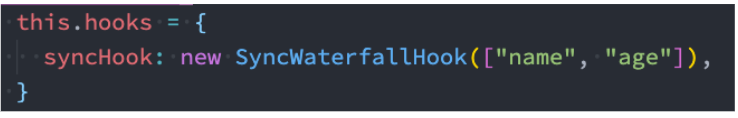
第二步:注册Hook中的事件
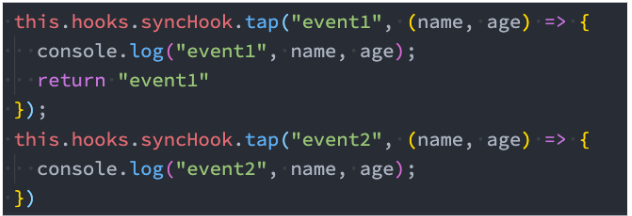
第三步:触发事件

javascript
const { SyncHook, SyncBailHook, SyncLoopHook, SyncWaterfallHook } = require("tapable");
const { AsyncSeriesHook, AsyncParallelHook } = require('tapable');
let counter = 0;
class HYLearnTapable {
constructor() {
this.hooks = {
// syncHook: new SyncHook(["name", "age"])
// bail: 在某一个事件监听的函数中, 如果有返回值, 那么后续的监听的事件就不会执行了
// syncHook: new SyncBailHook(["name", "age"])
// loop:在某个时间监听的函数中, 如果返回值为true, 那么这个回调函数就会循环执行.(返回undefined, 就停止执行)
// syncHook: new SyncLoopHook(["name", "age"])
// waterfall: 在某个时间监听的函数中, 如果有返回值, 那么它的返回值会作为下一次事件监听函数的第一个参数
syncHook: new SyncWaterfallHook(["name", "age"]),
// series: 在一个hook中, 监听了多次事件(多个回调函数), 这两个回调函数是串行执行
asyncHook: new AsyncSeriesHook(["name", "age"])
// parallel: 在一个hook中, 监听了多次事件(多个回调函数), 这两个回调函数是并行执行
// asyncHook: new AsyncParallelHook(["name", "age"])
}
// this.hooks.syncHook.tap("event1", (name, age) => {
// console.log("event1", name, age);
// return "event1";
// });
// this.hooks.syncHook.tap("event2", (name, age) => {
// console.log("event2", name, age);
// });
// this.hooks.asyncHook.tapAsync("event1", (name, age, callback) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// console.log("event1", name, age);
// callback();
// }, 2000);
// });
// this.hooks.asyncHook.tapAsync("event2", (name, age, callback) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// console.log("event2", name, age);
// callback();
// }, 2000);
// });
this.hooks.asyncHook.tapPromise("event1", (name, age) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("event1", name, age);
resolve();
}, 2000);
})
});
this.hooks.asyncHook.tapPromise("event2", (name, age) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("event2", name, age);
resolve();
}, 2000);
})
});
}
emit() {
// this.hooks.syncHook.call("why", 18);
// this.hooks.asyncHook.callAsync("kobe", 30, () => {
// console.log("第一次事件执行完成");
// });
this.hooks.asyncHook.promise("james", 33).then(() => {
console.log("事件监听完成");
});
}
}
const lt = new HYLearnTapable();
lt.emit();自定义Plugin
在之前的学习中,我们已经使用了非常多的Plugin:
- CleanWebpackPlugin
- HTMLWebpackPlugin
- MiniCSSExtractPlugin
- CompressionPlugin
- 等等
这些Plugin是如何被注册到webpack的生命周期中的呢?
第一:在webpack函数的createCompiler方法中,注册了所有的插件;
第二:在注册插件时,会调用插件函数或者插件对象的apply方法;
第三:插件方法会接收compiler对象,我们可以通过compiler对象来注册Hook的事件;
第四:某些插件也会传入一个compilation的对象,我们也可以监听compilation的Hook事件;
开发自己的插件
如何开发自己的插件呢?
目前大部分插件都可以在社区中找到,但是推荐尽量使用在维护,并且经过社区验证的;
这里我们开发一个自己的简单插件:将静态文件自动上传服务器中;
自定义插件的过程:
创建AutoUploadWebpackPlugin类;
编写apply方法:
- 通过ssh连接服务器;
- 删除服务器原来的文件夹;
- 上传文件夹中的内容;
在webpack的plugins中,使用AutoUploadWebpackPlugin类;
webpack.config.js
javascript
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const AutoUploadPlugin = require("./plugins/AutoUploadPlugin");
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/main.js",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "./build"),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin(),
new AutoUploadPlugin({
host: "123.207.32.32",
username: "root",
password: "",
removePath: "/root/test"
})
]
}plugins/AutoUploadPlugin.js
javascript
const { NodeSSH } = require('node-ssh');
class AutoUploadPlugin {
constructor(options) {
this.ssh = new NodeSSH();
this.options = options;
}
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.afterEmit.tapAsync("AutoUploadPlugin", async (compilation, callback) => {
// 1.获取输出的文件夹
const outputPath = compilation.outputOptions.path;
// 2.连接服务器(ssh连接)
await this.connectServer();
// 3.删除原来目录中的内容
const serverDir = this.options.remotePath;
await this.ssh.execCommand(`rm -rf ${serverDir}/*`);
// 4.上传文件到服务器(ssh连接)
await this.uploadFiles(outputPath, serverDir);
// 5.关闭ssh
this.ssh.dispose();
callback();
});
}
async connectServer() {
await this.ssh.connect({
host: this.options.host,
username: this.options.username,
password: this.options.password
});
console.log("连接成功~");
}
async uploadFiles(localPath, remotePath) {
const status = await this.ssh.putDirectory(localPath, remotePath, {
recursive: true,
concurrency: 10
});
console.log('传送到服务器: ', status ? "成功": "失败");
}
}
module.exports = AutoUploadPlugin;